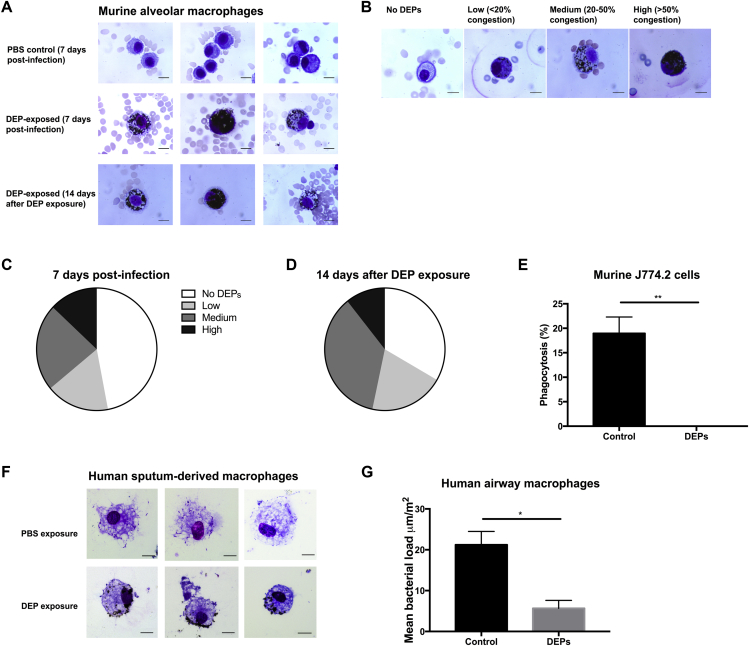
Fig 3.
DEP-congested alveolar macrophages have reduced phagocytic ability. A, Alveolar macrophages isolated by BAL from PBS- (top) and DEP- (middle) exposed mice 7 days postinfection. Alveolar macrophages isolated from DEP-exposed mice 14 days after the last DEP exposure (bottom), suggesting that clearance of DEPs from macrophages is a slow process. B, Scoring guide for alveolar macrophages according to how congested with DEPs they are. No uptake of DEPs, low (<20% of cell cytoplasm is congested with DEPs), medium (20% to 50% congestion), and high (>50% congestion) uptake were scored as shown. C, Proportion of alveolar macrophages graded as characterized by low, medium, or high congestion at day 7 postinfection following daily DEP exposure. D, Proportion of alveolar macrophages graded as characterized by low, medium, or high congestion 14 days after the last DEP exposure. E, Pneumococcal opsonophagocytic ability of mouse J774.2 macrophages treated with either PBS (control) or DEPs. F, Uptake of DEPs (bottom) versus control (PBS-treated) airway macrophages isolated from sputum of human volunteers. G, Phagocytosis of pneumococci by human airway macrophages pretreated with either PBS (control) or DEPs. Error bars indicate the SEM; ***P < .001; **P < .01; *P < .05. For each experimental condition, n = 3 to 5.