Figure 1.
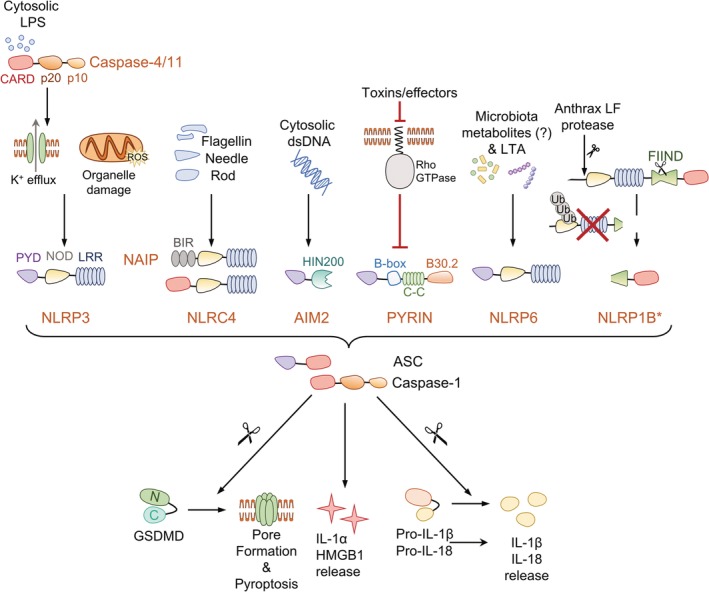
Inflammasome‐forming sensors and their known activators. Inflammasomes are multiprotein complexes that function as platforms to activate caspase‐1. Some inflammasome sensors, such as NLRP3, PYRIN and NLRP1B, are activated following perturbations of cellular homeostasis triggered by damage or microbial associated molecular patterns. For example, mitochondrial or lysosomal disruption will lead to NLRP3 activation, while inhibition of host Rho‐GTPases will allow PYRIN inflammasome assembly and degradation of the NLRP1B N‐terminal will lead to nucleation of the free CARD‐containing NLRP1B C‐terminus. Other inflammasome sensors, exemplified by AIM2, NAIP‐NLRC4 and caspase‐11 (caspase‐4 and 5 in humans), are activated in response to direct detection of their ligands: DNA is recognised by the AIM2 HIN200 domain, NAIP proteins bind flagellin and type 3 secretion system (T3SS) needles and rods, and the caspase‐11 CARD domain interacts with LPS. Active caspase‐11/4/5 cleaves Gasdermin D (GSDMD), leading to pore formation and subsequent potassium efflux, which can trigger non‐canonical activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome, and pyroptosis. NLRP6 functions as a direct sensor of lipoteichoic acid (LTA), but can also be activated by changes in the microbiota and has additionally been shown to perform inflammasome‐independent functions. *Human NLRP1 has an N‐terminal PYD domain. Domain compositions are colour coded and abbreviated as follows: CARD, caspase‐activation and recruitment domain; p20 and p10, large and small catalytic subunits; PYD, pyrin domain; NOD, nucleotide binding and oligomerisation domain; LRR, leucine rich repeat; BIR, baculovirus inhibitor of apoptosis domain; HIN200, haematopoietic expression, interferon inducible, nuclear localised (HIN) DNA binding domain of ∼200 residues; C‐C, coiled‐coil; FIIND, function to find domain
