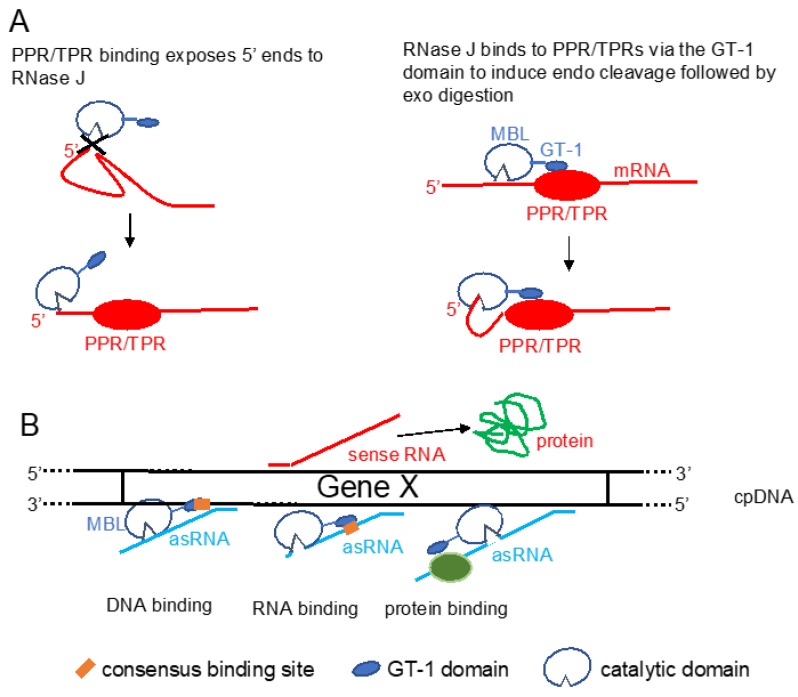
Figure 3.
Putative functions of the GT-1 domain in models for RNase J modes of action. (A) Two scenarios for chloroplast (cp) 5′-end maturation by RNase J and the corresponding RNA-binding protein (RBP). Left, the RNA 5′-end structure prevents RNase J access. Binding of the RBP induces a structural change, exposing the 5′ end to digestion. Right, RNase J is recruited to the 5′ end by direct binding to the RBP, perhaps via the GT-1 domain. (B) Possible mechanisms of GT-1 domain-mediated recruitment of RNase J to targeted asRNAs by binding to a DNA site near the asRNA transcription start (left), to the asRNA itself (center), or to an RNA-binding cofactor (right). PPR/TPR: pentatricopeptide/tetratricopeptide repeat-containing proteins.