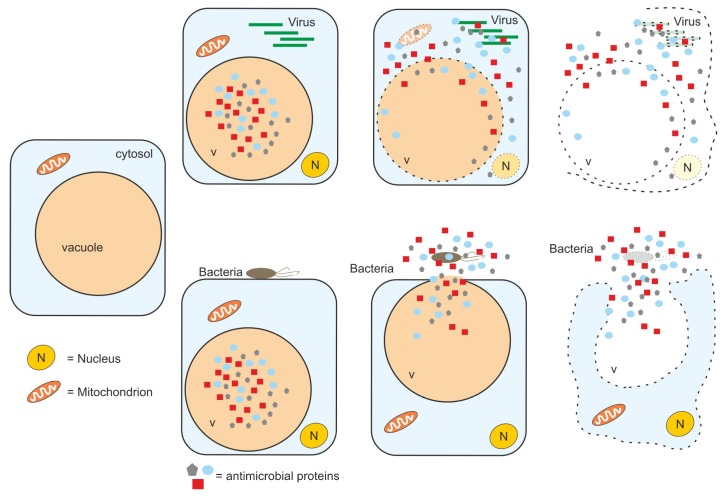
Figure 2.
Different release mechanisms of antimicrobial proteins accumulated in the vacuole. The collapse of the vacuolar membrane (tonoplast) upon pathogen invasion (e.g., viruses) leads to plant cell death. Fusion of the tonoplast with the PM leads to the release of antimicrobial proteins to the cell's exterior. This is effective against pathogens proliferating in the apoplast (like some bacteria) and delays cell death.