Figure 1.
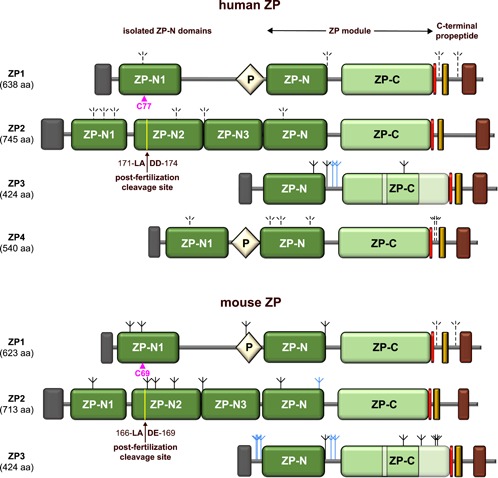
Scheme of the domain architecture of human and mouse ZP components. The positions of the conserved ZP1‐specific Cys essential for filament cross‐linking (Nishimura et al., 2019) and the post‐fertilization cleavage site of ZP2 important for ZP hardening (Gahlay, Gauthier, Baibakov, Epifano, & Dean, 2010) are marked by magenta arrowheads and black arrows, respectively. Dark gray rectangle, SP; light yellow diamond, trefoil/P domain; red rectangle, CFCS; dark yellow rectangle, EHP; brown rectangle, transmembrane domain. The locations of the two ZP3‐specific subdomain elements within the protein's ZP‐C domain, based on the structure of chicken ZP3 (Han et al., 2010), are indicated by a lighter shading. Experimentally supported (Boja et al., 2003; Chalabi et al., 2006; Raj et al., 2017; Zhao et al., 2004) and predicted carbohydrates are depicted as solid and dashed inverted tripods, respectively, with N‐glycans colored black and O‐glycans colored blue. aa, amino acids, CFCS, consensus furin cleavage site; EHP, external hydrophobic patch; SP, signal peptide; ZP, zona pellucida
