Figure 2.
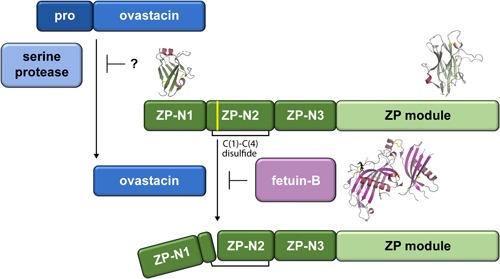
Scheme of the pathway regulating the cleavage of mammalian ZP2. Activation of pro‐ovastacin by a serine protease triggers site‐specific cleavage of ZP2, yielding two protein fragments that remain covalently attached via the predicted C1–C4 disulfide bond of ZP2 ZP‐N2 (indicated by a black bracket). ZP2 cleavage inactivates the sperm‐binding activity of the ZP as well as increases its resistance to α‐chymotrypsin digestion. Premature processing of ZP2 is counteracted by serum glycoprotein fetuin‐B, which inhibits ovastacin and thus, ZP2 cleavage. Structural information is available for ZP2 ZP‐N1 (PDB ID 5II6), ZP2 ZP‐C (PDB ID 5BUP), and fetuin‐B (PDB ID 6HPV). Note that in this figure, as well as in Figure 3, the ZP module is represented by a single rounded rectangle
