Figure 3.
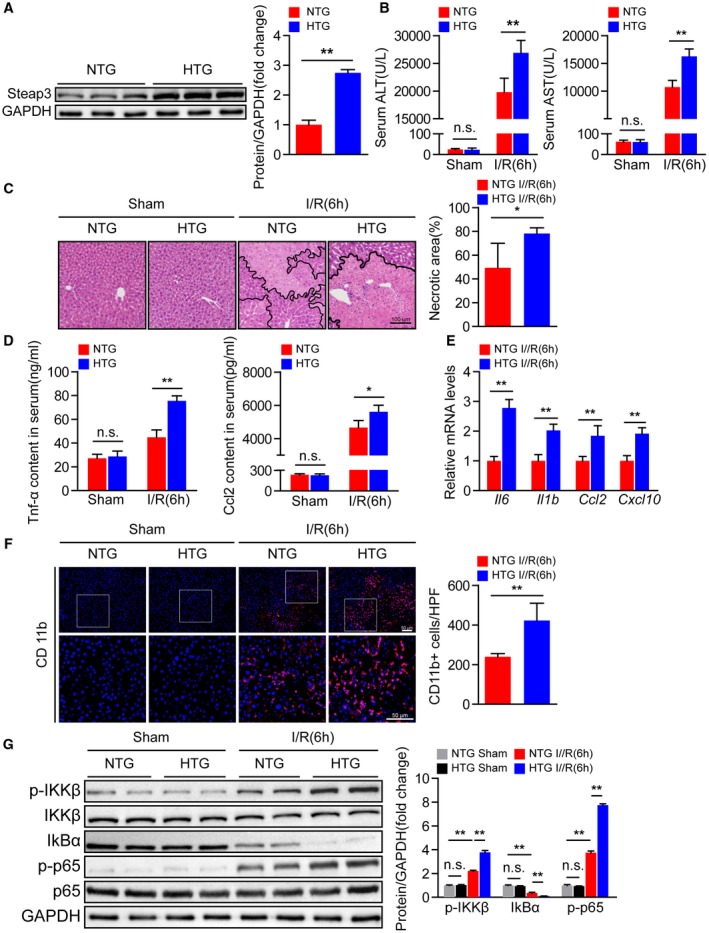
Hepatocyte‐specific Steap3 overexpression aggravates inflammatory responses and liver damage during hepatic I/R injury. (A) Steap3 protein expression in the liver of NTG and Steap3‐HTG mice. GAPDH served as the loading control (n = 3/group). (B) Serum ALT/AST activities in NTG and Steap3‐HTG mice at 6 hours after hepatic I/R operation (n = 8/group). (C) Representative histological H&E‐stained images and statistics showing necrotic areas in liver tissue from NTG and Steap3‐HTG mice at 6 hours after hepatic I/R operation (n = 6/group). Scale bar, 100 μm. (D) Serum levels of inflammatory factors (Tnf‐α and Ccl2) in NTG and Steap3‐HTG mice at 6 hours after hepatic I/R operation (n = 6‐8/group). (E) mRNA levels of proinflammatory factors (Il6, Il1b, Ccl2, and Cxcl10) in the liver of NTG and Steap3‐HTG mice at 6 hours after hepatic I/R operation (n = 6/group). (F) Representative CD11b immunofluorescence staining in the liver lobes of NTG and Steap3‐HTG mice at 6 hours after hepatic I/R operation (n = 5/group). Scale bar, 50 μm. (G) Protein levels of NF‐κB signaling pathway molecules in the liver of NTG and Steap3‐HTG mice at 6 hours after hepatic I/R operation. GAPDH served as the loading control (n = 3/group). All data are presented as the mean ± SD. Levels of statistical significance are indicated as *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01. For statistical analysis, one‐way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s post hoc analysis or Tamhane’s T2 post hoc analysis and two‐tailed Student t test were used. Abbreviations: HPF, high‐power field; IκBα, inhibitory κBα; IKKβ, IκB kinase β; n.s., not statistically significant.
