Figure 4.
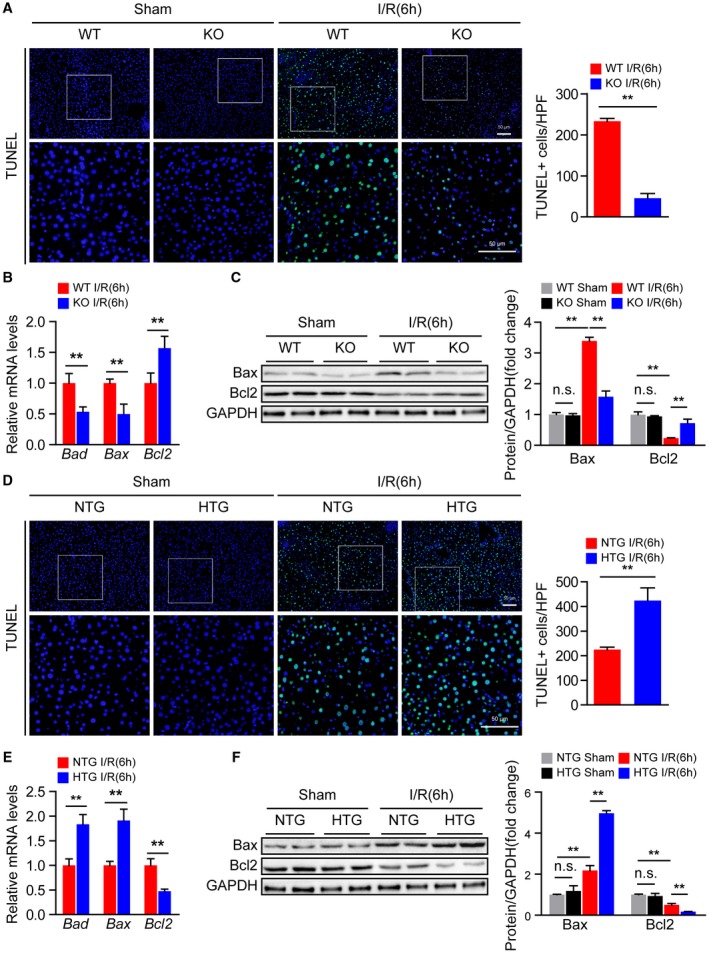
Steap3 promotes apoptosis during hepatic I/R injury. (A) TUNEL staining in liver sections from WT and Steap3‐KO mice at 6 hours after hepatic I/R operation (n = 4/group). Scale bar, 50 μm. (B) mRNA levels of apoptosis‐related genes (Bad, Bax, and Bcl2) in liver samples of WT and Steap3‐KO mice at 6 hours after hepatic I/R operation (n = 6/group). (C) Western blot analysis of the Bax and Bcl2 levels in the liver of WT and Steap3‐KO mice at 6 hours after hepatic I/R operation. GAPDH served as a loading control (n = 3/group). (D) TUNEL staining in liver sections of NTG and Steap3‐HTG mice at 6 hours after hepatic I/R operation (n = 4/group). Scale bar, 50 μm. (E) mRNA levels of apoptosis‐related genes (Bad, Bax, and Bcl2) in liver samples from NTG and Steap3‐HTG mice at 6 hours after hepatic I/R operation (n = 6/group). (F) Western blot analysis of the Bax and Bcl2 levels in the liver of NTG and Steap3‐HTG mice at 6 hours after hepatic I/R operation. GAPDH served as a loading control (n = 3/group). All data are shown as the mean ± SD. Levels of statistical significance are indicated as *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01. For statistical analysis, one‐way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s post hoc analysis or Tamhane’s T2 post hoc analysis and two‐tailed Student t test were used. Abbreviations: HPF, high‐power field; n.s., not statistically significant.
