Figure 5.
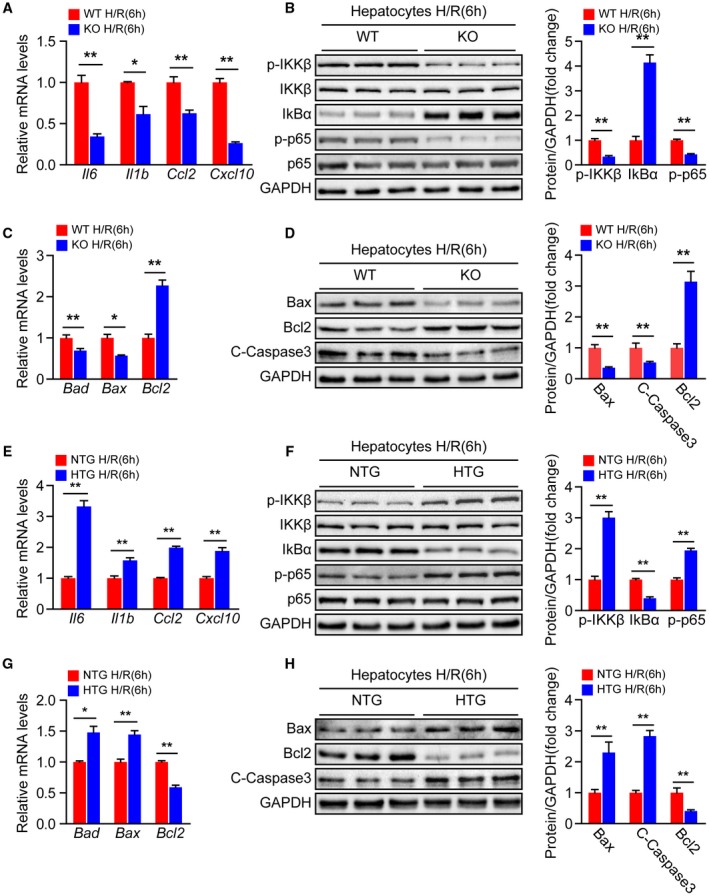
Steap3 accelerates hepatocyte inflammation and apoptosis during hepatic I/R injury. (A) mRNA levels of proinflammatory factors (Il6, Il1b, Ccl2, and Cxcl10) in cultured primary hepatocytes isolated from WT and Steap3‐KO mice that were subjected to H/R challenge (n = 3/group). (B) Protein levels of NF‐κB signaling pathway molecules in cultured primary hepatocytes isolated from WT and Steap3‐KO mice that were challenged by H/R insult. GAPDH served as the loading control. Representative of three independent experiments. (C) mRNA levels of apoptosis‐related genes (Bad, Bax, and Bcl2) in cultured primary hepatocytes isolated from WT and Steap3‐KO mice that were subjected to H/R challenge (n = 3/group). (D) Western blot analysis of the Bax, Bcl2, and cleaved caspase‐3 levels in cultured primary hepatocytes isolated from WT and Steap3‐KO mice that were challenged by H/R insult. GAPDH served as the loading control. Representative of three independent experiments. (E) mRNA levels of proinflammatory factors (Il6, Il1b, Ccl2, and Cxcl10) in cultured primary hepatocytes isolated from NTG and Steap3‐HTG mice that were subjected to H/R challenge (n = 3/group). (F) Protein levels of NF‐κB signaling pathway molecules in cultured primary hepatocytes isolated from NTG and Steap3‐HTG mice that were challenged by H/R insult. GAPDH served as the loading control. Representative of three independent experiments. (G) mRNA levels of apoptosis‐related genes (Bad, Bax, and Bcl2) in cultured primary hepatocytes isolated from NTG and Steap3‐HTG mice that were subjected to H/R challenge (n = 3/group). (H) Western blot analysis of the Bax, Bcl2, and cleaved caspase‐3 levels in cultured primary hepatocytes isolated from NTG and Steap3‐HTG mice that were challenged by H/R insult. GAPDH served as the loading control. Representative of three independent experiments. All data are shown as the mean ± SD. Levels of statistical significance are indicated as *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01. For statistical analysis, a two‐tailed Student t test was used. Abbreviations: IκBα, inhibitory κBα; IKKβ, IκB kinase β.
