Figure 6.
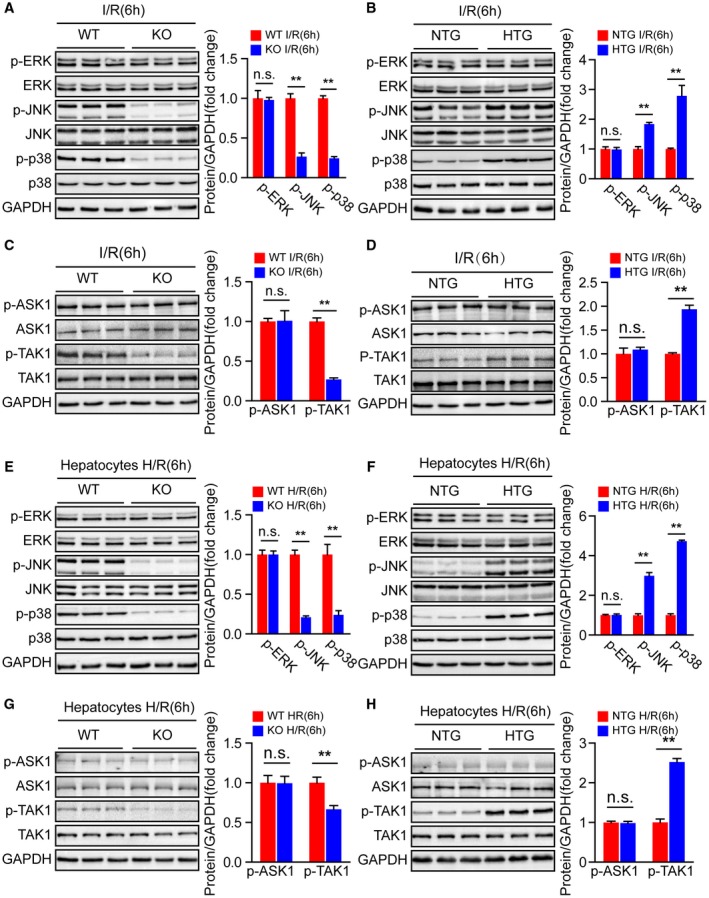
Steap3 deficiency inhibits TAK1/JNK/p38 signaling in liver injury. (A,B) Western blot analysis of the total and phosphorylated protein expression levels of classic MAPKs in the liver of Steap3‐KO (A) and Steap3‐HTG (B) mice after hepatic I/R operation (n = 3/group). (C,D) Western blot analysis of the total and phosphorylated protein expression levels of classic MAPK kinase kinases (MAP3Ks), including TAK1 and ASK1, in the liver of Steap3‐KO (C) and Steap3‐HTG (D) mice after hepatic I/R operation (n = 3/group). (E,F) Western blot analysis of the total and phosphorylated protein expression levels of classic MAPKs in cultured primary hepatocytes isolated from Steap3‐KO (E) and Steap3‐HTG (F) mice that were challenged by H/R insult. Representative of three independent experiments. (G,H) Western blot analysis of the total and phosphorylated protein expression levels of classic MAP3Ks, including TAK1 and ASK1, in cultured primary hepatocytes isolated from Steap3‐KO (G) and Steap3‐HTG (H) mice that were challenged by H/R insult. Representative of three independent experiments. For (A‐H), GAPDH served as the loading control. All data are shown as the mean ± SD. Levels of statistical significance are indicated as *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01. For statistical analysis, a two‐tailed Student t test was used. Abbreviations: ERK, extracellular signal–regulated kinase; n.s., not statistically significant.
