Figure 2.
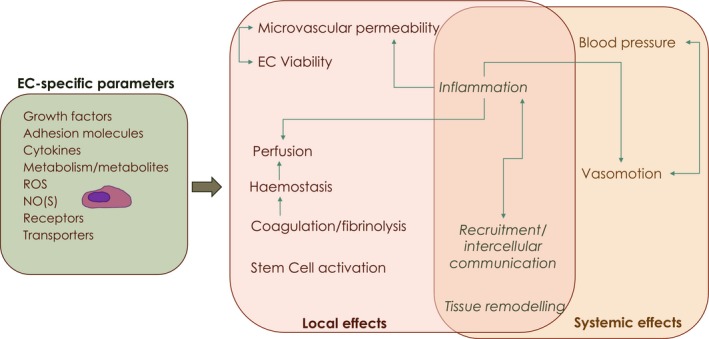
Summary of local and systemic effects of specific EC parameters. Endothelial cells possess diverse combinations in surface receptors and transporters, as well as diffusible secretory compounds, which include growth factors (such as VEGF) and metabolites, which will be determined by intrinsic endothelial properties and tissue microenvironment/substrate availability; receptors, transporters and signalling molecules such as reactive oxygen species (ROS) or nitric oxide (NO), downstream of endothelial or inducible nitric oxide synthases (NOS), are also variables contributing to EC heterogeneity and plasticity. All these parameters are specific to individual capillary networks, but oscillate, in a more or less transient fashion, in response to local and systemic pressures. These alterations in endothelial behaviour, signalling and metabolic activity subsequently modulate local tissue microenvironment as well as systemic circulation patterns.
