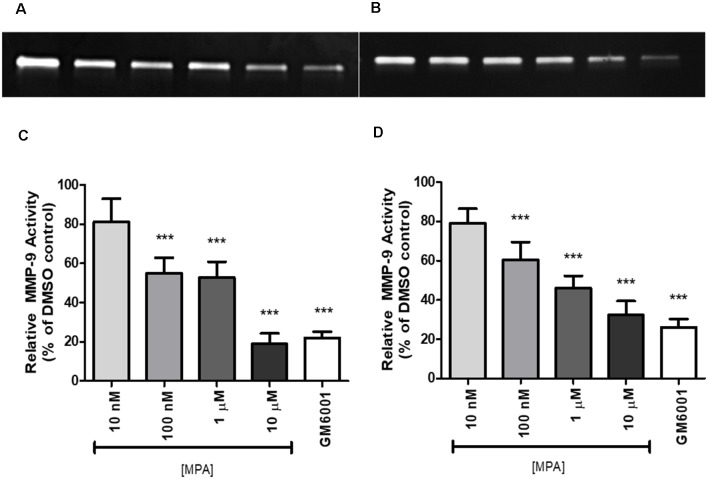
Figure 1.
Medroxyprogesterone Acetate (MPA) reduced the gelatinolytic activity of MMP-9 in C6 glial cells. (A,B) Representative zymograms showing MMP-9 activity of MPA-treated conditioned media (CM) determined by gelatin zymography. After a 48-h (left) or 72-h (right) incubation period in serum-free media, supernatants obtained from 1 × 106 cells were analyzed by gelatin zymography. DMSO at 0.1% was used as the vehicle control and constitutively showed MMP-9 gelatinolytic activity (lane 1). Upon MPA treatment, MMP-9 gelatinolytic activity was significantly decreased (lanes 2–5). GM6001 (lane 6) was used as a negative control for active MMP-9. (C,D) Densitometric analysis of conditioned media from astroglia determined by gelatin zymography. C6 glial cells were incubated for 48-h (left) or 72-h (right) with increasing concentrations of MPA and GM6001, a non-specific MMP inhibitor. Results are expressed as percentage of activity of treated to untreated cells (mean ± SEM). MMP-9 gelatinolytic activity of untreated cells is expressed as 100%. MPA significantly decreased MMP-9 enzymatic activity in a dose-dependent manner (P < 0.001) compared with that found in untreated cells. The results are representative of five independent experiments. ***p < 0.001.