Figure 2: Wingless and EGFR signaling pathways.
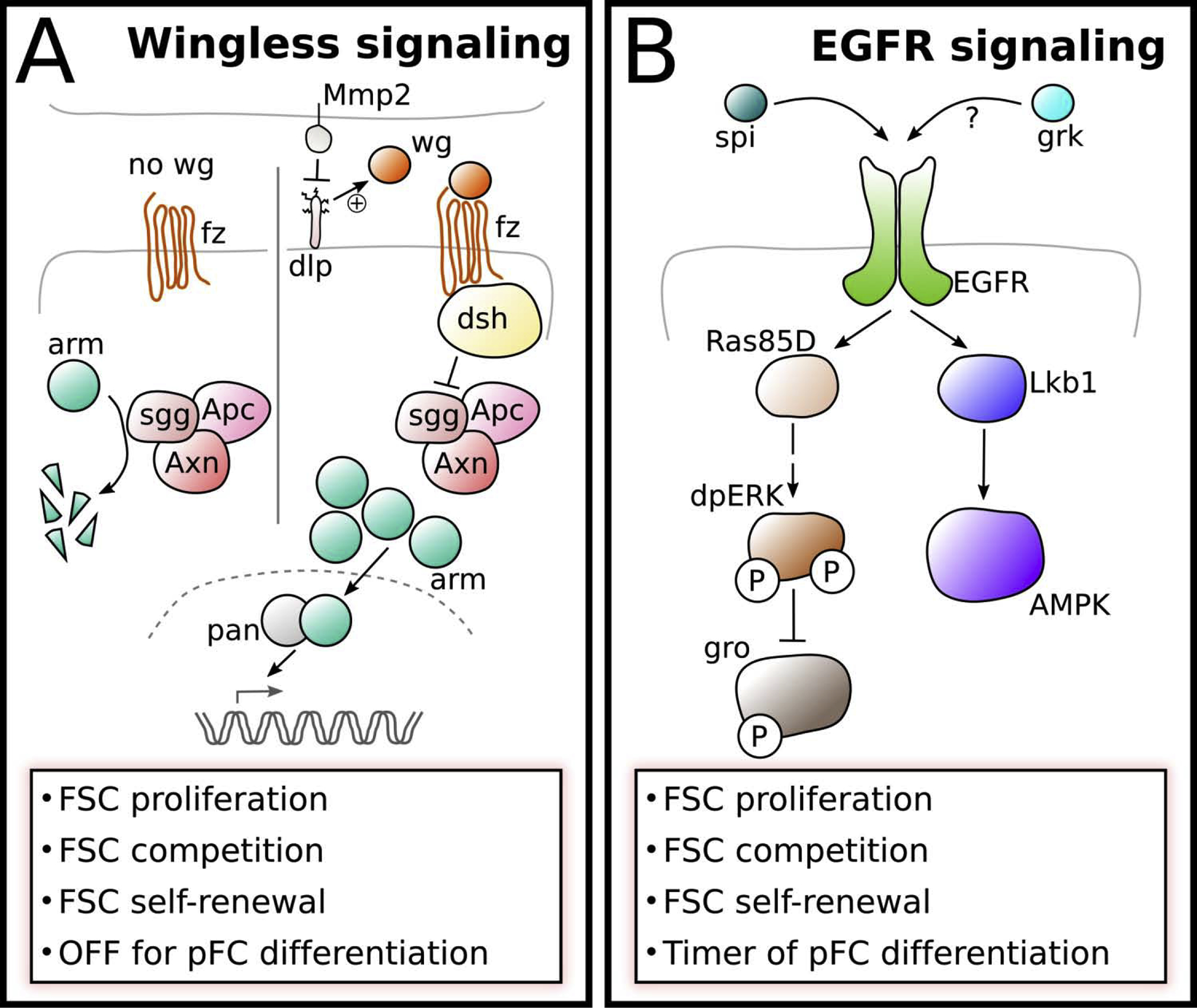
A) Wg is provided to FSCs by IGS cells leading to high levels of Wnt pathway activity in FSCs, which changes dynamically [17,19]. The glypican Dlp aids to concentrate Wg in the niche region and is counteracted by Matrix metalloproteinase 2 (Mmp2). In the absence of Wg ligand, Arm is subject to proteasomal degradation induced by a destruction complex consisting of Apc, Shaggy (Sgg) and Axin (Axn). When Wg binds to its receptor Frizzled (Fz), active Dishevelled (Dsh) represses destruction complex activity allowing arm to interacts with Pangolin (Pan) to activate target gene expression.
B) The expression of the EGFR ligand Spitz (Spi) is induced by Wnt signaling in the FSC. It is unclear whether Gurken (Grk) may also function as an EGFR ligand in the FSCs. EGFR signaling is active in FSCs, uniformly low in newly produced pFCs and active again in older pFCs and main body follicle cells. In FSCs activated EGFR signaling induces the MAP-Kinase pathway resulting in the dual-phosphorylation and activation of ERK. One target of dpERK is Groucho (Gro), which is repressed by ERK-mediated phosphorylation and functions as a molecular timer regulating pFC differentiation. Active EGFR signaling is also required for the establishment of cell polarity via the Lkb1-AMPK pathway.
