Figure 1. Silencing of yrbF-B occurs upon host entry and colonization fitness varies inversely with transporter activity.
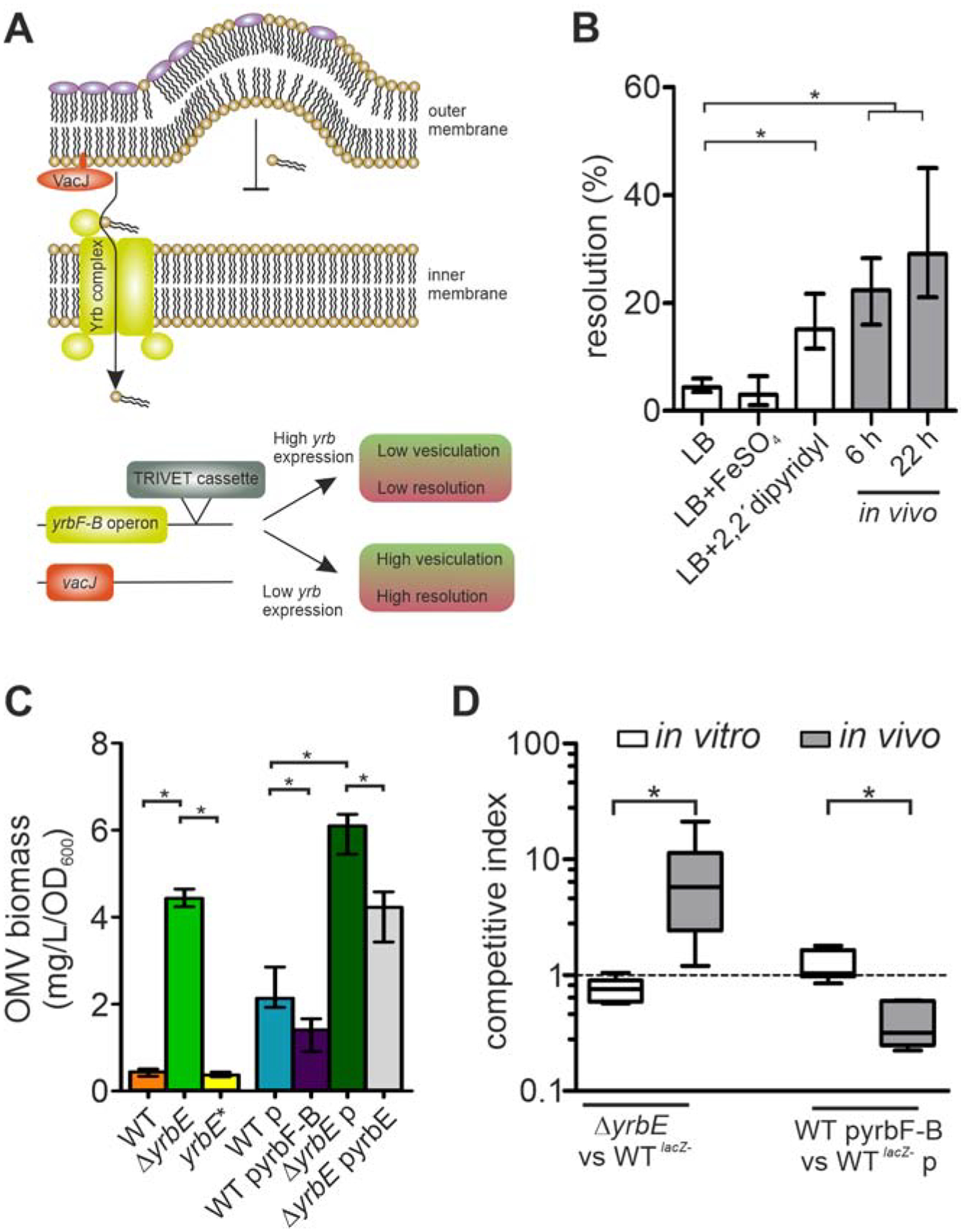
(A) Schematic overview of the phospholipid transporter encoded by the vacJ and yrbFEDCB (yrbF-B operon) genes. The VacJ/Yrb transporter (also known as Mla system) shuttles phospholipids from the outer membrane (OM) back to the inner membrane. High expression is associated with low vesiculation, while low expression or inactivation of the transporter results in phospholipid accumulation in the OM outer leaflet promoting vesiculation. Insertion of the TRIVET reporter cassette downstream of the yrb-locus allows monitoring of its transcriptional activity using excision of an antibiotic resistance cassette (resolution) as a readout.
(B) Transcriptional regulation of the yrbF-B operon was analyzed by the recombination-based in vivo reporter system TRIVET, which results in increased reporter resolution upon transcriptional repression of the yrbF-B operon (Cakar et al., 2018). Shown are resolution frequencies of strain Vc_res1_TRIVET yrbF::tpc grown for 22 h in regular LB, LB with high-(FeSO4) or low-(2,2’-dipyridyl) iron concentrations, as well as in vivo 6 and 22 h post-infection. Shown is median ± interquartile range (IQR) (n = 6; *P < 0.05). See also Figure S1.
(C) OMV quantification (Bradford) for WT, ΔyrbE, yrbE*, WT with empty vector (p), WT with yrbF-B overexpression plasmid (pyrbF-B), ΔyrbE with empty vector (p) and ΔyrbE with expression plasmid (pyrbE) after 8 h cultivation. Shown is median ± IQR (*P < 0.05) with the following number of biological replicates: n = 9 for WT and WT p; n = 6 for ΔyrbE, yrbE*, ΔyrbE p and ΔyrbE pyrbE; n = 8 for WT pyrbF-B.
(D) Competition indices of in vitro (LB) and in vivo (murine model) assays are shown as boxplot with whiskers (*P < 0.05) with the following number of biological replicates: n = 8 for all in vitro competitions, n = 10 for the in vivo competitions of WTlacZ− and ΔyrbE as well as n = 6 for the in vivo competitions of WTlacZ− p and WT pyrbF-B. Strains used for the competition are indicated on the x-axis.
