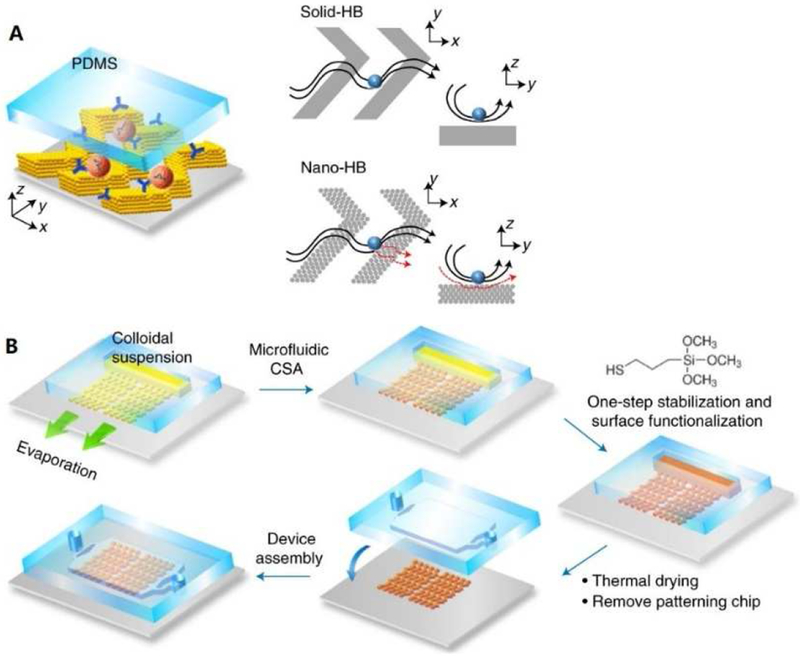
Figure 10.
(A) Schematic of the MINDS strategy that improves biosensing by 3D nanostructuring of microfluidic elements, such as the herringbone mixer. The conventional, solid-HB mixer creates microvortices to promote mass transfer of targets. A particle will experience hydrodynamic resistance near a solid surface that reduces direct surface contact. In a 3D nano-HB chip, fluid near the surface can be drained through the porous structure (red dashed lines) to increase the probability of particle-surface collisions. (B) Workflow for fabricating a 3D nano-HB chip by MINDS. Reprinted with permission from Ref. 116. Copyright 2019, Springer Nature.