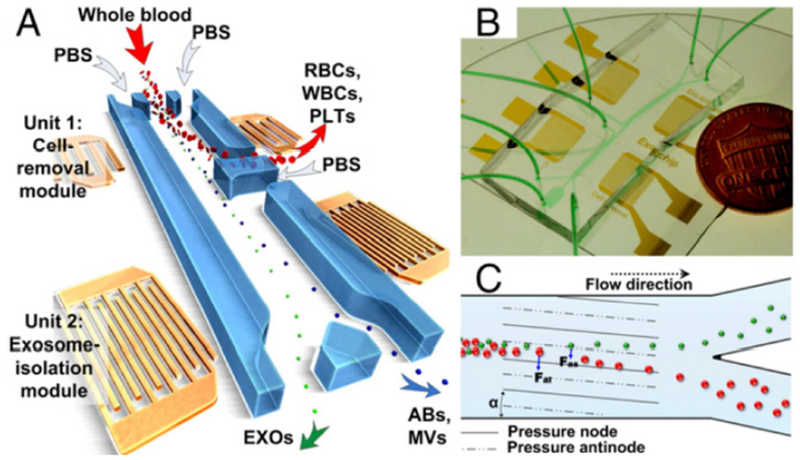
Figure 5.
Overall schematic for acoustofluidic enrichment of exosomes. (A) RBCs, WBCs, and PLTs are depleted from whole blood through Unit 1 to provide cell-free plasma in downstream analysis. The filtrate containing total extracellular vesicles is further filtered through Unit 2, where exosomes are segregated from ABs and MVs. (B) Optical image of fully integrated acoustofluidic chip. (C) Size-based separation occurs in each module due to the lateral deflection induced by a taSSAW field. The periodic distribution of pressure nodes and antinodes generates an acoustic radiation force to push large particles toward node planes. Abbreviations: RBC = red blood cell, WBC = white blood cell, PLT = platelet, AB = apoptotic body, MV = microvesicle, taSSAW = tilted-angle standing SAW. Reprinted with permission from Ref. 111. Copyright 2017, National Academy of Sciences.