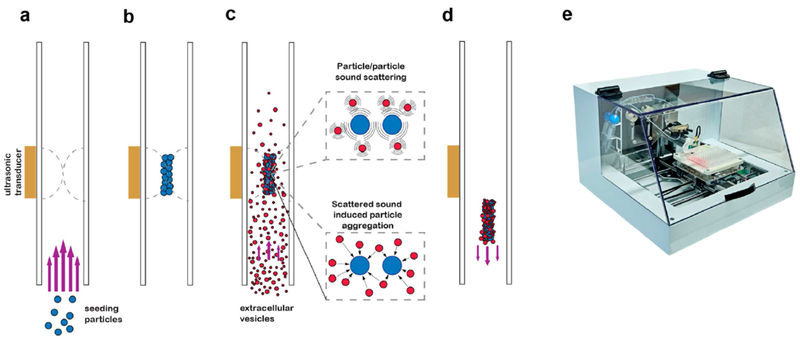
Figure 6.
Mechanistic scheme of acoustic trapping for extracellular vesicle isolation. (a) Seeding particles are introduced into the fluidic channel and (b) are packed together by the acoustic standing wave generated by the ultrasonic transducer. Excess seeding particles are washed away. (c) Total extracellular vesicles (EV’s) are introduced into the fluidic channel and are trapped by the seed cluster via secondary acoustic forces and particle-particle interactions. (d) After cleaning, the seed cluster-EV aggregate is released upon terminating the acoustic wave. (e) Photograph of the automated trapping device, AcouTrap. Reprinted with permission from Ref. 112. Copyright 2018, American Chemical Society.