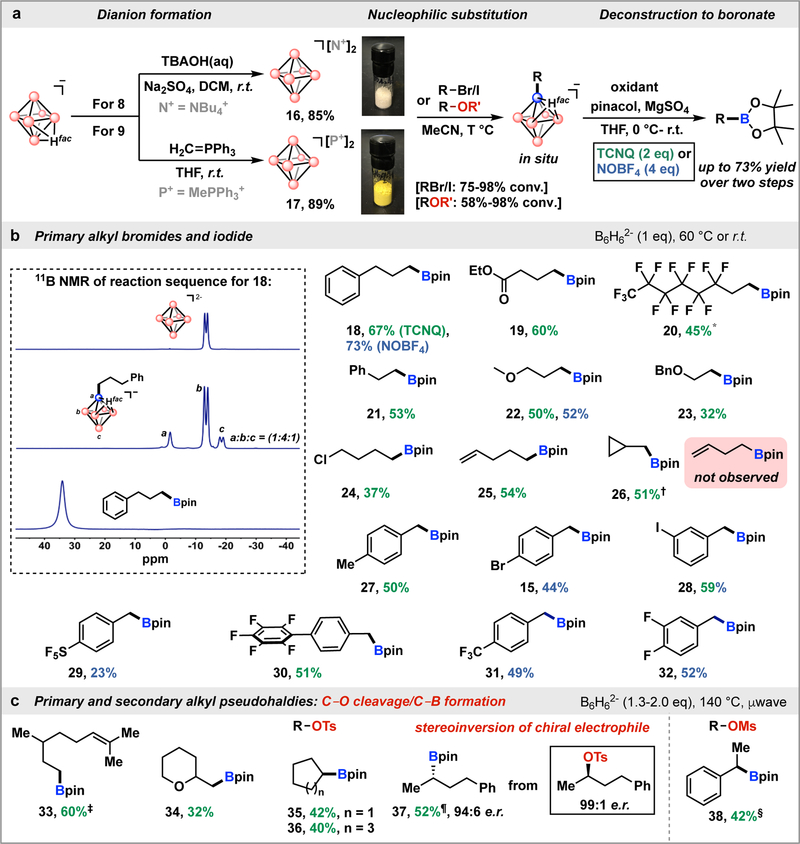
Fig. 3. Borylation/cage deconstruction strategy with dianionic closo-hexaborates.
a, Preparation of B6H62− reagents and their subsequent use in borylation of organic electrophiles. b, Substrate scope of alkyl halides. Standard reaction conditions: B6H62− (1.0 equiv), alkyl halide (0.4 mmol, 1.0 equiv), MeCN (2 mL). For unactivated alkyl bromides, 60 °C heating. For benzyl bromides, room temperature. Pinacol (10 equiv), MgSO4 (12 equiv), THF (2 mL), 0 °C to room temperature for deconstruction. Isolated yields are calculated after cage deconstruction. Inset: 11B NMR spectra for the synthesis sequence: closo-hexaborate dianion (top); monosubstituted closo-hexaborate (middle); purified alkyl‒Bpin (bottom). c, Substrate scope of alkyl pseudohalides. Reaction conditions: B6H62− (1.3–2.0 equiv), µwave heating at 140 °C. † Using alkyl iodide (2 equiv). † B6H62− (1.5 equiv) and µwave heating at 110 °C. ‡ Using oil bath heating at 80 °C. ¶ µwave heating at 90 °C. § Using oil bath heating at 60 °C. [N +] = NBu4+, [P+] = MePPh3+