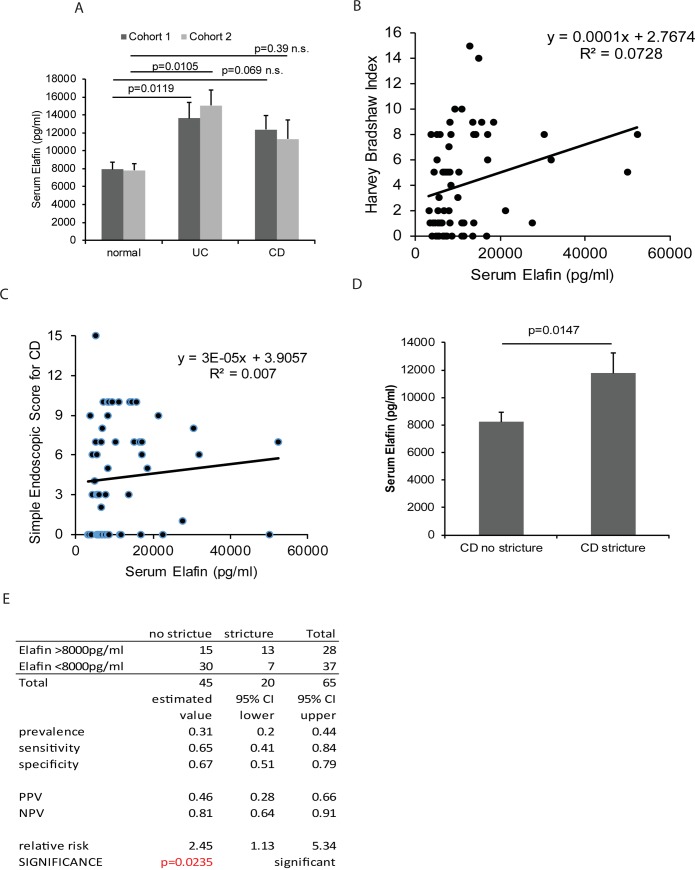
Fig 1. Circulating elafin levels are increased in IBD patients.
(A) Serum elafin levels of 50 normal, 23 UC, and 28 CD patients in cohort 1 and 20 normal, 57 UC, and 67 CD in cohort 2. Multiple group comparisons were done by one-way ANOVA. (B) Scatter plot shows the moderate correlation between serum elafin levels and clinical disease activity (HBI) in 68 CD patients. (C) Scatter plot shows no association between serum elafin levels and endoscopic disease activity (SES-CD) in 68 CD patients. (D) The stricturing CD patients (n = 20) had significantly higher serum elafin levels than non-stricturing CD patients (n = 45) in a combined dataset. Two-group comparison was done by Student’s t-test. (E) Prevalence, sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value, negative predictive value, and relative risk of elafin test for indicating intestinal stricture in CD patients.