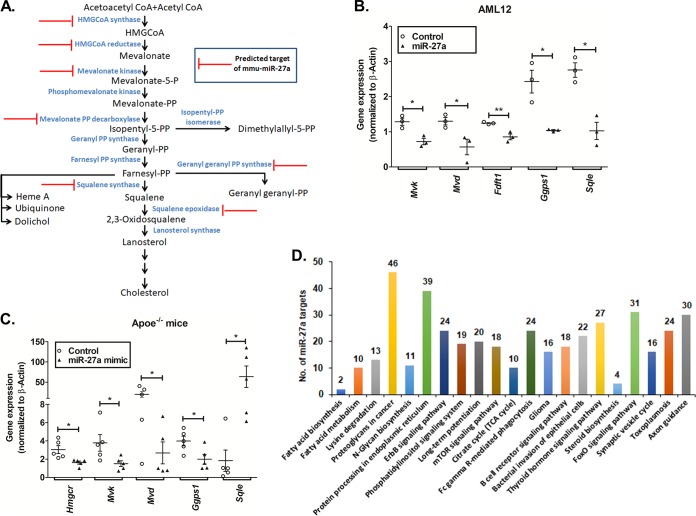
FIG 9.
Augmentation of miR-27a represses multiple genes in the cholesterol biosynthesis pathway. (A) Potential targets of miR-27a in the cholesterol biosynthesis pathway predicted by miRWalk, RNAhybrid, and TargetScan were categorized based on their molecular functions using the PANTHER database. (B and C) qPCR analysis of predicted genes in AML12 cells (n = 3) (B) and liver tissues of high-cholesterol-diet-fed Apoe−/− mice (C) transfected or injected with the miR-27a mimic or the control oligonucleotide (n = 5 to 6 animals per group). Statistical significance was determined by Student’s t test (unpaired, 2 tailed). *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01 (compared to the control group). (D) Pathway analysis for miR-27a targets was performed using TargetScan (in silico predictions) and mirPath v3 (validated interactions). Twenty-one pathways were commonly enriched by both these tools, including steroid biosynthesis, fatty acid metabolism, and biosynthesis. This analysis further demonstrates that miR-27a regulates lipid metabolism. The number of genes targeted by miR-27a in each of these pathways is indicated above each bar. TCA, tricarboxylic acid.