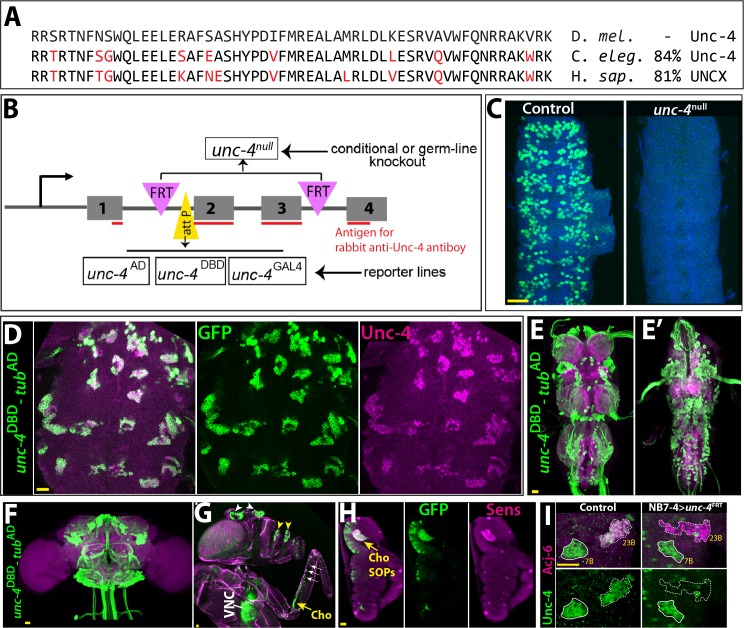
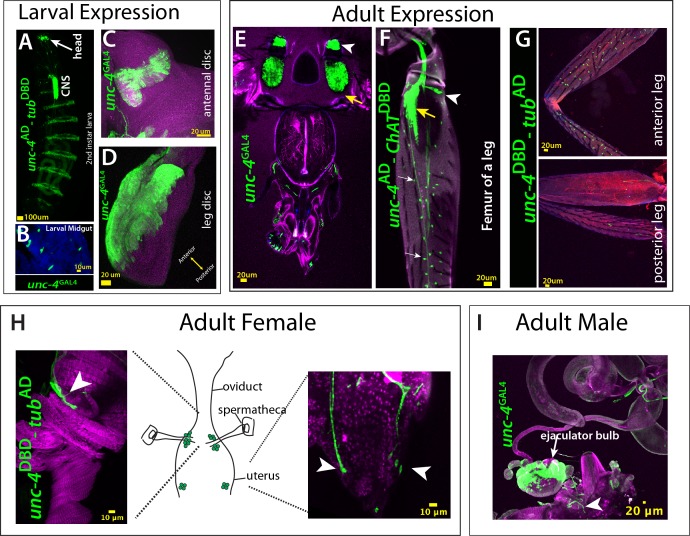
Figure 1. Tools generated to study Unc-4 function.
(A) Homeodomains of Unc-4 protein in D. melanogaster, C. elegans and H. sapiens are shown with the percent identity on the right. Amino acids that differ from Drosophilase quence were highlighted in red. (B) Schematic representation of edited unc-4 locus in unc-4FRT line shown (drawing is not to scale). Two FRT sites (magenta) are present with the same orientation flanking 2nd and 3rd exons (the homeodomain coding exons) and an attP site (yellow) is located 5’ to the second exon. unc-4null fly line was generated by FLP/FRT mediated excision of these exons in the germline. The same FLP/FRT mediated excision in somatic tissues was used for conditional mutant analysis. Trojan exons were inserted into the attP site to generate unc-4AD, unc-4DBD, unc-4GAL4 reporter lines. The region that is recognized by rabbit Unc-4 antibody underlined in red. (C) Dissected VNC samples from control (left) and unc-4null (right) embryos are shown. In the control VNC, Unc-4 protein (green) is expressed in a segmentally-repeated pattern. In the mutant embryo, no Unc-4 expression is detected. (D–H) unc-4DBD-tubAD driven GFP expression (green) shown. (D) Expression of this split GAL4 combination overlaps with Unc-4 protein expression (magenta) in the larval VNC. The clusters of neurons correspond to ventrally located Unc-4+ hemilineages. (E–F) Unc-4 is expressed in clusters of neurons in the adult VNC (E, E’) and brain (F). Ventrally located VNC lineages shown in E; dorsally located VNC lineages shown in E’. Here and in other figures, CadN antibody staining (magenta) used to define the contours of the adult CNS tissues. (G) Anterior body parts of an adult fly shown. Unc-4 reporter marks different types of sensory neurons: chordotonal (cho) organ (yellow arrow) and bristle sensory (white arrows) neurons in the leg, olfactory neurons in maxillary pulps (yellow arrowheads) and antennas (white arrowheads), and Johnston’s organ (not visible in this image). Magenta is cuticle autofluorescence. (H) A leg disc from an early stage pupa shown; anterior is to the left. Unc-4 is expressed in progenitors of chordotonal neurons, also called sensory organ precursors (SOPs), which were marked with Sens expression (magenta). (I) An example for conditional removal of unc-4 shown. Unc-4 (green) and Acj6 (magenta) are co-expressed in 23B neurons in the larval VNC but only Unc-4 is expressed in 7B neurons. NB7-4 specific FLP expression in the unc-4FRT larva (right panel) removes Unc-4 expression from the 23B neurons (NB7-4 progeny) but not the 7B neurons. Anterior is up in all images in this and other figures unless indicated otherwise. Scale bar (yellow line) is 20 microns.