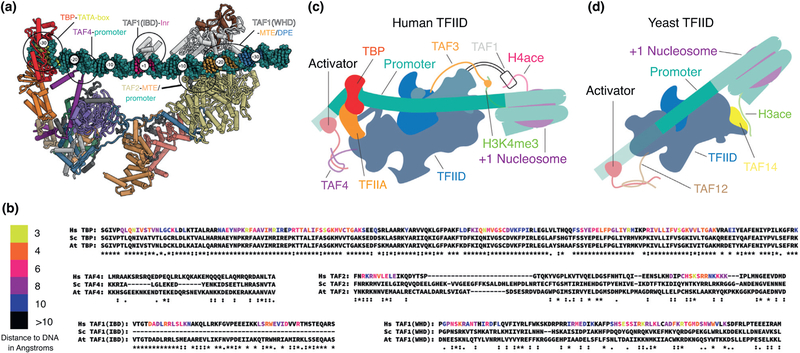
Figure 5.
Evolutionary comparison of TFIID elements involved in interactions with DNA, activators and histone modifications. (a) Atomic model of human TFIID bound to promoter DNA, with subunits colored according to the code at the bottom of Figure 1. Major points of interaction of TFIID with promoter DNA are highlighted. (b) Sequence alignment of the regions that interact with promoter DNA as seen in human TFIID for human, yeast (Saccharomyces cerevisiae) and plant (Arabidopsis thaliana). Residues are colored based on the distance to the DNA in the model of human TFIID bound to promoter DNA, except for the TAF4 region proximal to the promoter for which the sequence register could not be determined. Alignment scores for the TAF1 Inr binding domain (IBD) was calculated using only the human and A. thaliana sequences, as S. cerevisiae lacks this domain entirely. (c) Model of interactions of human TFIID with chromatin marks on the +1 nucleosome and with upstream activators. (d) Model of interaction of yeast TFIID with chromatin marks on the +1 nucleosome and with upstream activators.