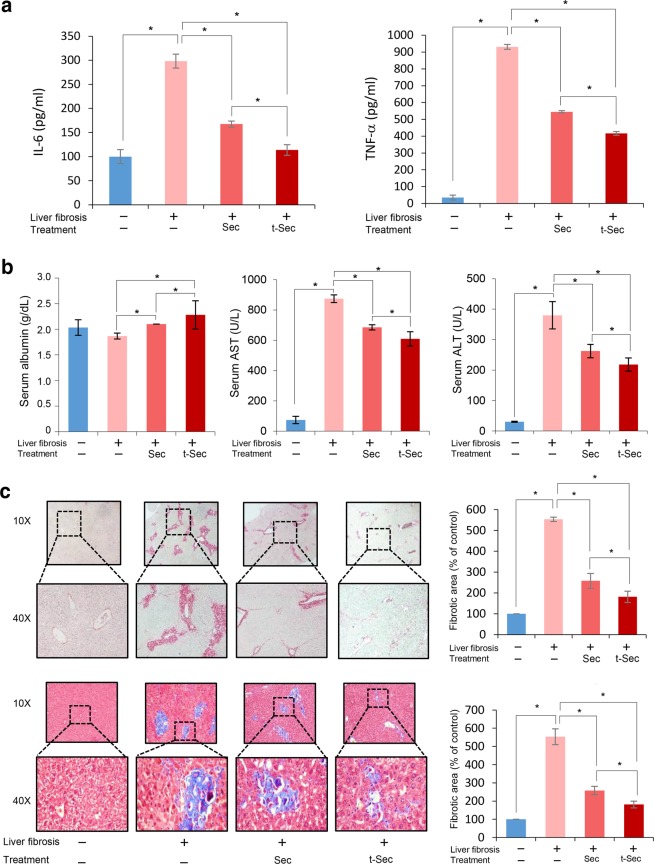
Fig. 4. Determination of systemic inflammation and a histological assessment of liver specimens.
a ELISA results demonstrating the serum levels of proinflammatory mediators, including IL-6 and TNF-α, in each group. Secretome infusions significantly reduced the serum levels of IL-6 and TNF-α in mice with liver fibrosis. When comparing both groups, miR-150 secretome infusion induced more significant reductions in these cytokines than those of the control secretome infusion group. b Serum levels of albumin, AST, and ALT in each group. The serum albumin concentration was highest in the miR-150 secretome group, followed by the control secretome group. Of the TAA-treated groups, the miR-150 secretome group showed the lowest levels of these liver enzymes, followed by the control secretome group. c Sirius red [Top left] and Masson trichrome [Bottom left] staining showing the degree of fibrosis. Both stains demonstrated that infusion of the miR-150 secretome decreased liver fibrosis more than that of infusion of the control secretome. [Right] Comparison of fibrotic areas in each group. Percentages of fibrotic areas were measured using NIH ImageJ and are expressed as relative values to those in normal livers. The values are presented as the mean ± standard deviation of three independent experiments. *P < 0.05. ALT alanine transaminase, AST aspartate transaminase, Sec the secretome obtained from ASCs after 48 h of incubation, TNF-α tumor necrosis factor-α, t-Sec the secretome released from miR-150-transfected ASCs.