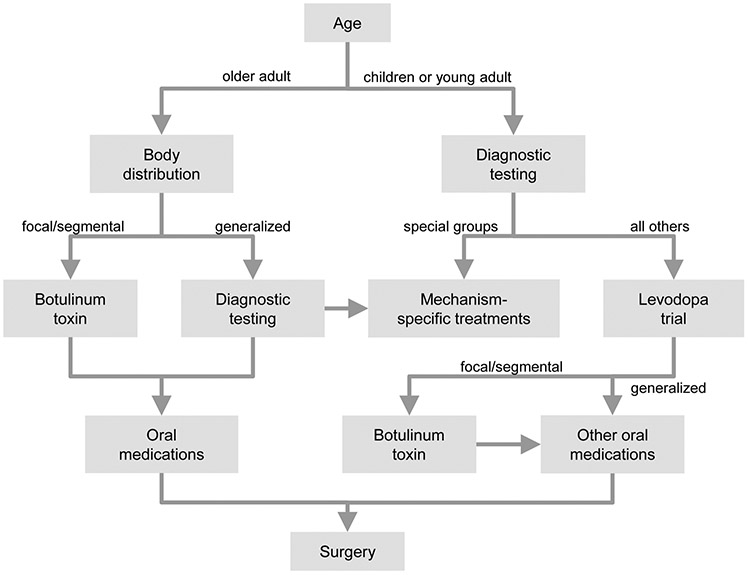
Figure 3. Treatment approach.
This algorithm provides a basic strategy for the therapeutic approach to most patients with dystonia. The clinical and etiological evaluations are important, because They influence optimal treatments strategies. For children, diagnostic testing is essential because there is a greater likelihood of discovering a treatable cause. When a cause cannot be found, a trial of oral levodopa is conducted to rule out dopa-responsive dystonia. For adults, dystonia is more often idiopathic, so extensive workup is often not needed. Instead, the approach depends on body distribution. For the focal dystonias, botulinum toxins provide a useful starting point. Oral medications can be used, but often are not well-tolerated. Those who have unsatisfactory responses can be offered surgery. Generalized dystonias or dystonia combined with other neurological problems in adults requires some additional diagnostic testing, to disclose a potentially treatable cause.