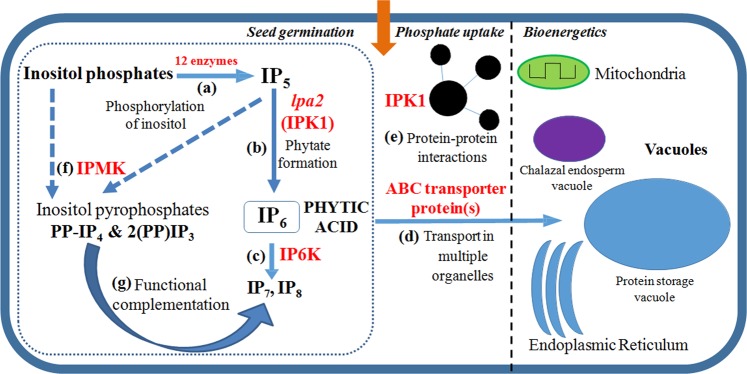
Figure 1.
A model of key components of inositol phosphate pathway involving IPK1. (a) myo-Inositol is converted to inositol phosphates, including IP5 via 12 enzymes. (b) IPK1 then phosphorylates IP5 to IP6 or phytic acid. (c) IP6K phosphorylates phytic acid to higher forms like IP7 and IP8. (d) Phytic acid is transported to different organelles via ABC transporter proteins into storage vacuole, chalazal endosperm vacuole and endoplasmic reticulum. (e) IPK1 is involved in protein-protein interactions with other proteins, which are involved in seed germination, phosphate uptake and bioenergetics. (f) Inositol phosphate multi-kinase ( IPMK) converts IP5 and other inositol phosphates to inositol pyrophosphates PP-IP4 and 2(PP)-IP3. (g) Inositol pyrophosphates PP-IP4 and 2(PP)-IP3 are capable of mediating functions carried out by IP7 and IP8, which would not be formed in the event of absence of IP6. IPK1 itself, rather than a single transporter protein or an upstream enzyme, appears to be the most promising target for low-phytate maize.