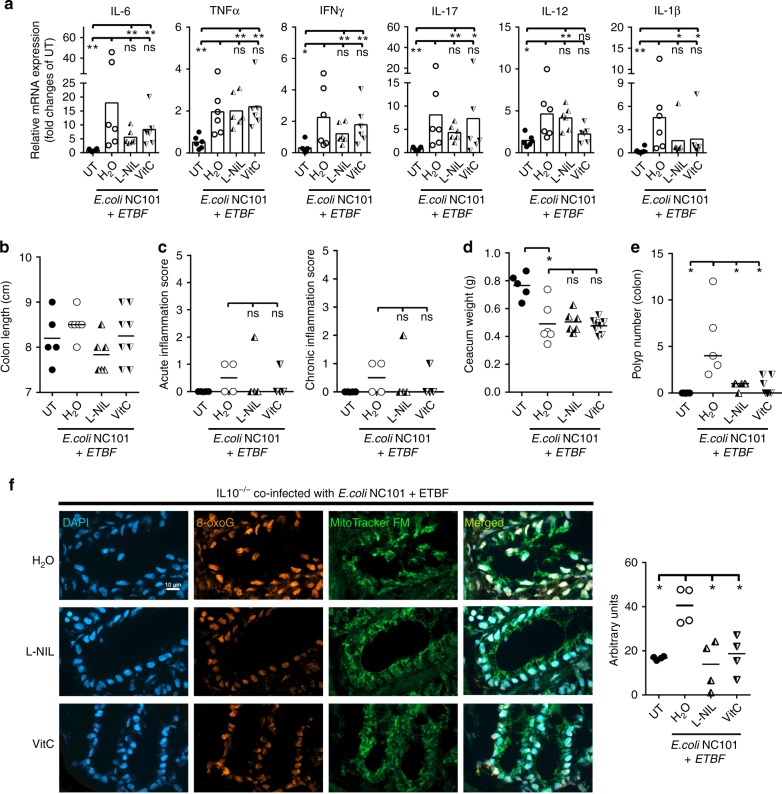
Fig. 5. Antioxidants reduce E. coli NC101 + ETBF-induced polyposis in IL10 −/− mice.
a Four-week-old IL10−/− mice were inoculated by oral gavage with E. coli NC101 and ETBF, and treated or untreated with L-NIL or VitC for 8 weeks. cDNA levels of indicated inflammatory cytokines were quantified by qPCR. Relative mRNA expression was normalized to 1 for untreated IL10−/− mice. N = 24 mice were examined. Colon length b, acute inflammation and chronic inflammation c, cecum weight d, and colonic polyp number e were measured in 12-week-old IL10−/− mice of the indicated treatments. N = 25 mice were examined. f Immunofluorescence for 8-oxoG and MitoTracker in colon from E. coli NC101 and ETBF-infected IL10−/− mice administered with L-NIL or VitC. Magnification 100×. Scale bar = 10 µm. Right panel: quantification of 8-oxoG immunofluorescence shown to the left. One dot represents the median intensity of fluorescence of 40 nuclei per mouse as shown in Supplementary Fig. 5c. N = 16 samples were examined over three independent experiments. All data were analyzed using the two-sided non-parametric t-test Mann–Whitney; *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01; ns nonsignificant.