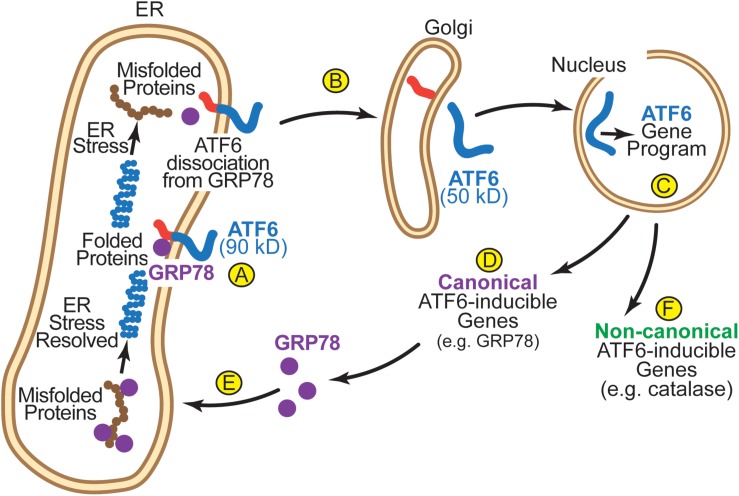
FIGURE 3.
(A) In its inactivated state, ATF6 is a 90 kD ER transmembrane protein that is anchored in the membrane by GRP78. (B) Upon ER stress, GRP78 dissociates from the ER luminal domain of ATF6, which allows the 90 kD form of ATF6 to translocate to the Golgi, where is it cleaved by S1P and S2P to liberate the N-terminal approximately 400 amino acids (50 kD) of ATF6 from the ER membrane. (C) The clipped form of ATF6 has a nuclear localization sequence, which facilitates its movement to the nucleus where it binds to specific regulatory elements in ATF6-responsive genes, such as ER stress response elements (ERSEs), and induces the ATF6 gene program. (D) The canonical ATF6 gene program comprises genes that encode proteins that localize to the ER, such as the chaperone, GRP78 (E), where they fortify ER protein folding. (F) The non-canonical ATF6 gene program comprises genes that encode proteins not typically categorized as ER stress-response proteins, such as catalase, which localize to regions of the cell outside the ER.