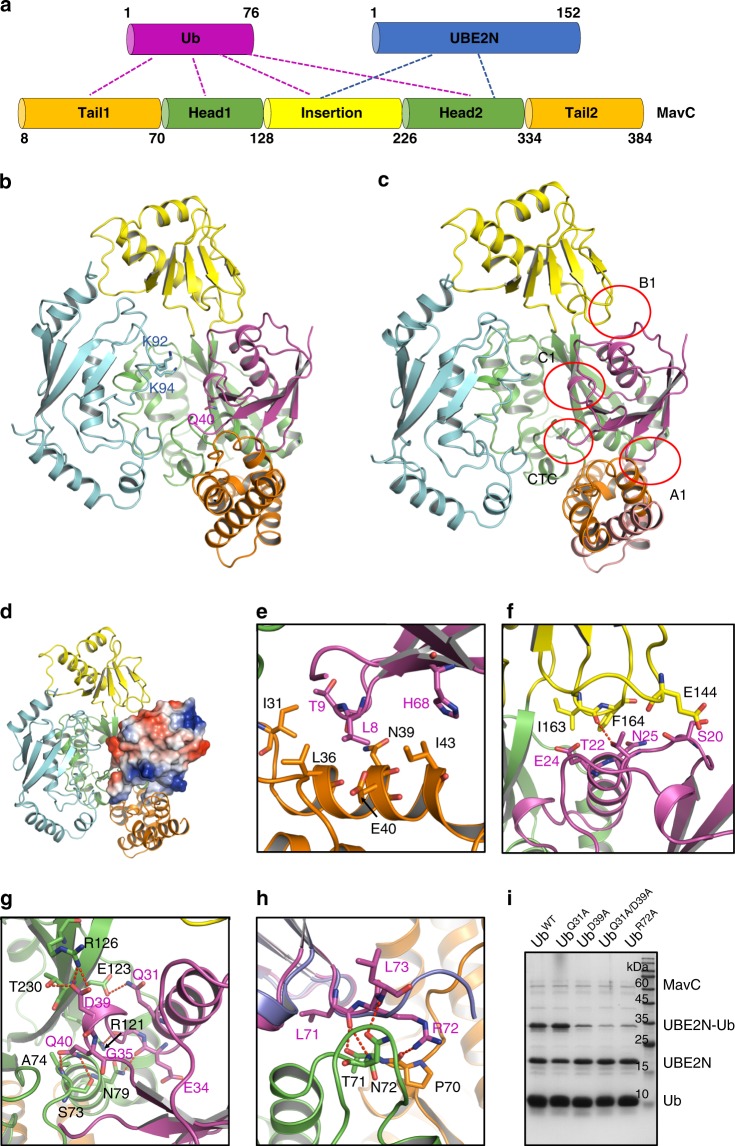
Fig. 1. Overall structure of the MavC/UBE2N/Ub complex.
a Domain architecture of MavC showing interaction modes among MavC, UBE2N, and Ub. b Overall structure of the MavC/UBE2N/Ub complex, colored as in a. Q40 of Ub, K92 and K94 of UBE2N are shown as sticks. c Overview of the interfaces between MavC and Ub in the MavC/UBE2N/Ub complex. d Overall structure of the MavC/UBE2N/Ub complex, with Ub shown in the electrostatic surface model. e–g Detailed interfaces of MavC–Ub interaction as marked in c, including A1 e, B1 f and C1 g. Hydrogen bonds are represented as red dashed lines. h Detailed CTC interface of MavC–Ub interaction as marked in c. Ub in the CHBP/Ub structure is colored in blue, and aligned to that in the MavC/UBE2N/Ub complex. i Mutations of the MavC-interacting residues in Ub decreased its ability in MavC-catalyzed ubiquitination. Ub and its mutants were incubated with MavC and UBE2N for 1 h at 37 °C. Then the samples were subjected to Tricine gel, followed by Coomassie blue staining. Source data are provided as a Source Data file. The experiment was repeated independently three times with similar results.