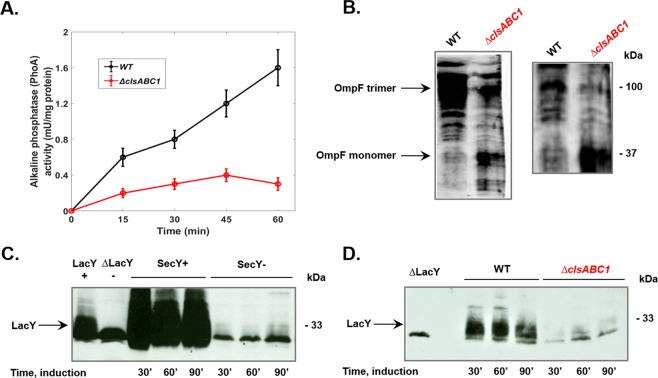
Figure 2.
CL-lacking E. coli cells are severely impaired in protein insertion into and translocation across the IM. (A) Protein translocation of alkaline phosphatase is reduced in the absence of CL. The alkaline phosphatase enzymatic assay was used to monitor translocation across the IM of wild type (WT) W3110 (black line and CL-lacking BKT12 ΔclsABC1 cells (red line). The efficiency of secretion of alkaline phosphatase was estimated by the indirect measurement of enzymatic activity in the periplasm as it is described in Materials and Methods. (B) The trimeric assembly pathway of OM β-barrel precursor OmpF is impaired in CL-lacking cells. Western blot analysis of total membrane fraction was utilized to assay co-translational translocation and maturation of this trimeric porin within the cell envelope with two different monomer-specific anti E.coli OmpF monoclonal antibodies. (C) Insertion yield of LacY was assayed in cold-sensitive secY39ts mutant, which is well known for the rapid temperature response in vivo and impaired translocation activity at low temperatures76 to support the contention that LacY is inserted into IM a SecY dependent manner. The ∆LacY lane shows a non-LacY band that crossreacts with LacY-specific antibody. (D) Insertion yield of LacY was determined after induction of its synthesis in WT W3110 and BKT12 ΔclsABC1. Native copy of lacY gene was carried on plasmid pT7-5 (AmpR) and expressed under OPtac regulation as previously described74. Immunoreacting LacY bands were visualized by ECL and quantified by BioRad imager and software. Broadening of LacY and OmpF protein bands is due to incomplete denaturation of membrane proteins and presence of multiple folding intermediates.