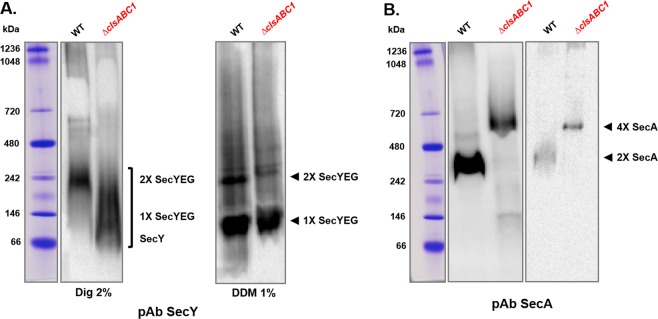
Figure 4.
The translocon in WT E. coli membranes is organized as a SecYEG dimer, which is unstable in CL-lacking cells due to lack of this lipid or dissociation of SecA. The BN-PAGE pattern of the SecYEG (A) and SecA complexes (B) are altered in CL-deficient E. coli cells, indicating that CL is involved in the stability or organization of the translocase complexes. The IMs from wild-type E. coli W3110 and mutant BKT12 ΔclsABC were solubilized with 2% digitonin (1 μg digitonin/μg protein) or 1% DDM, separated by BN-PAGE, transferred to nitrocellulose membranes and immunostained with antibodies against SecY, SecE and SecG (the core subunits of the SecYEG translocon, A) and SecA (a peripheral component of translocon, B). For each lane 25 μg of IM protein was loaded. Immune staining was carried out with all 3 antibodies individually. All three antibodies recognized a single complex running at about 230 kDa, but only the Western blot of BN-PAGE-separated proteins immunostained with anti-SecY is shown. (B) Immunoreacting SecA assemblies were visualized at different loading concentations.