Fig. 2. CD8+ T cells are crucial for the improved abscopal effect achieved by blocking/absence of β2-adrenergic signaling in CT26 colon carcinoma model.
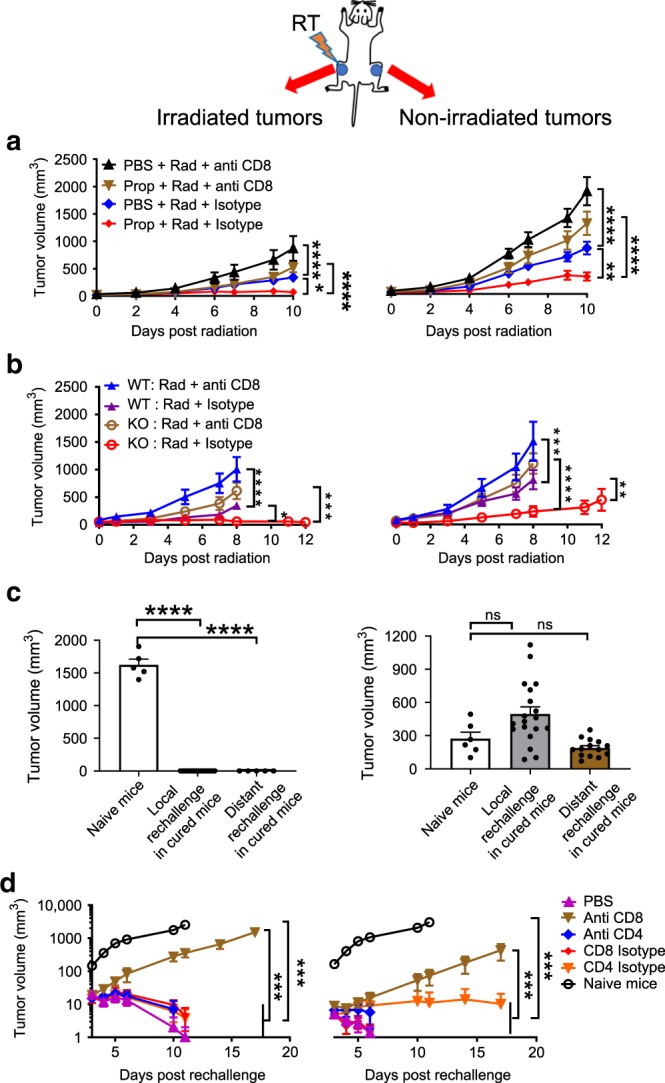
a and b Growth of irradiated (left) and non-irradiated (right) tumors in irradiated WT mice treated with or without propranolol a and irradiated WT mice and β2-AR KO mice b, which were depleted of CD8+ T cells. c The tumor growth of local and distant rechallenges with CT26 (left) and 4T1 (right) in mice cured by radiation plus propranolol compared with naïve mice. d The tumor growth (a log scale) of local (left) and distant (right) rechallenges with CT26 in mice cured by radiation and propranolol depleted of CD8+ or CD4+ T cells. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; ****P < 0.0001; ns = not significant (two-way ANOVA analysis for a, b, d; one-way ANOVA analysis for c). For a, n = 10 biologically independent mice in all groups; for b, n = 9 biologically independent mice in WT Rad + anti-CD8 and WT Rad + isotype groups, n = 8 biologically independent mice in KO Rad + anti-CD8 group, n = 10 biologically independent mice in KO Rad + isotype group; for CT26 model in c, n = 5 biologically independent mice in naïve mice group, n = 16 biologically independent mice in local rechallenge in cured mice group, n = 5 biologically independent mice in distant rechallenge in cured mice group; for 4T1 model in c, n = 6 biologically independent mice in naïve mice group, n = 19 biologically independent mice in local rechallenge in cured mice group, n = 14 biologically independent mice in distant rechallenge in cured mice group; for d, n = 6 biologically independent mice in PBS, anti-CD8, anti-CD4, CD8 isotype, and CD4 isotype groups, n = 5 biologically independent mice in naïve mice group.
