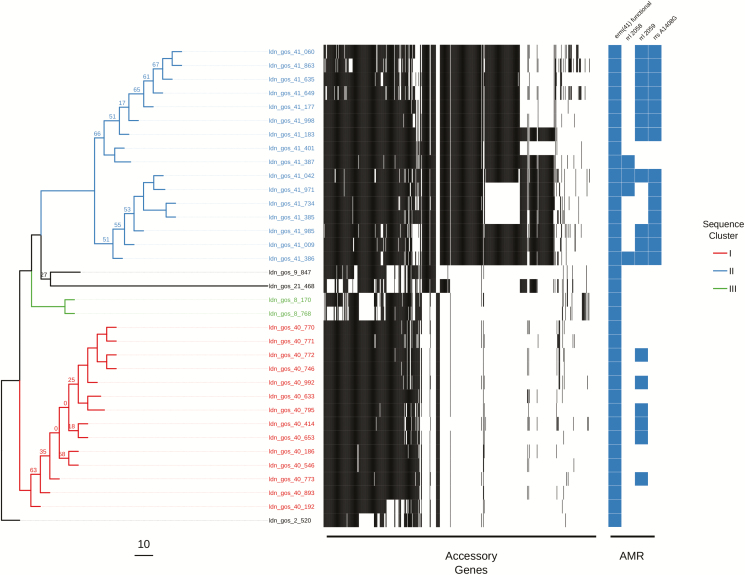
Figure 3.
Maximum likelihood SNV tree for all ST-26 isolates. SNVs were identified from mapping reads to a de novo assembled study isolate genome (ldn_gos_2_520). Samples are highlighted based on inclusion in sequence clusters. The tree is annotated with the presence (black) and absence (white) of accessory genes, as well as the presence of AMR-associated genes and mutations. This includes the presence of a functional erm(41) gene conferring inducible resistance to macrolides; the presence of 2 rrl mutations conferring high-level macrolide resistance; and the presence of a mutation in rrs conferring high-level amikacin resistance. The scale bar represents the number of SNVs and the node bootstrap scores below are shown if below 75. Abbreviations: AMR, antimicrobial resistance; SNV, single nucleotide variant.