Figure 4.
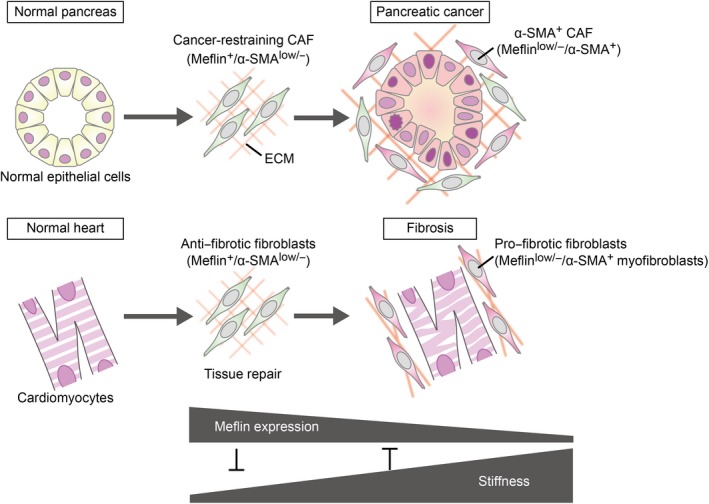
Analogy of cancer‐restraining cancer‐associated fibroblasts (rCAF) in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) to antifibrotic fibroblasts in cardiac fibrosis. In pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC), Meflin marks CAF that first emerge around metaplastic or transformed cells, which we showed behave as rCAF and later give rise to α‐SMA+ CAF with low Meflin expression, resulting in CAF heterogeneity in an advanced stage of cancer (upper panel). In cardiac infarction and fibrosis, we speculate that Meflin+ fibroblasts first proliferate in the injured area, and later yield α‐SMA+ myofibroblasts in the fibrotic phase (lower panel). The primary function of Meflin+ fibroblasts is to promote tissue repair and inhibit fibrosis, whereas loss of Meflin expression results in the differentiation of fibroblasts to myofibroblasts that contribute to the stiffening of cardiac tissue
