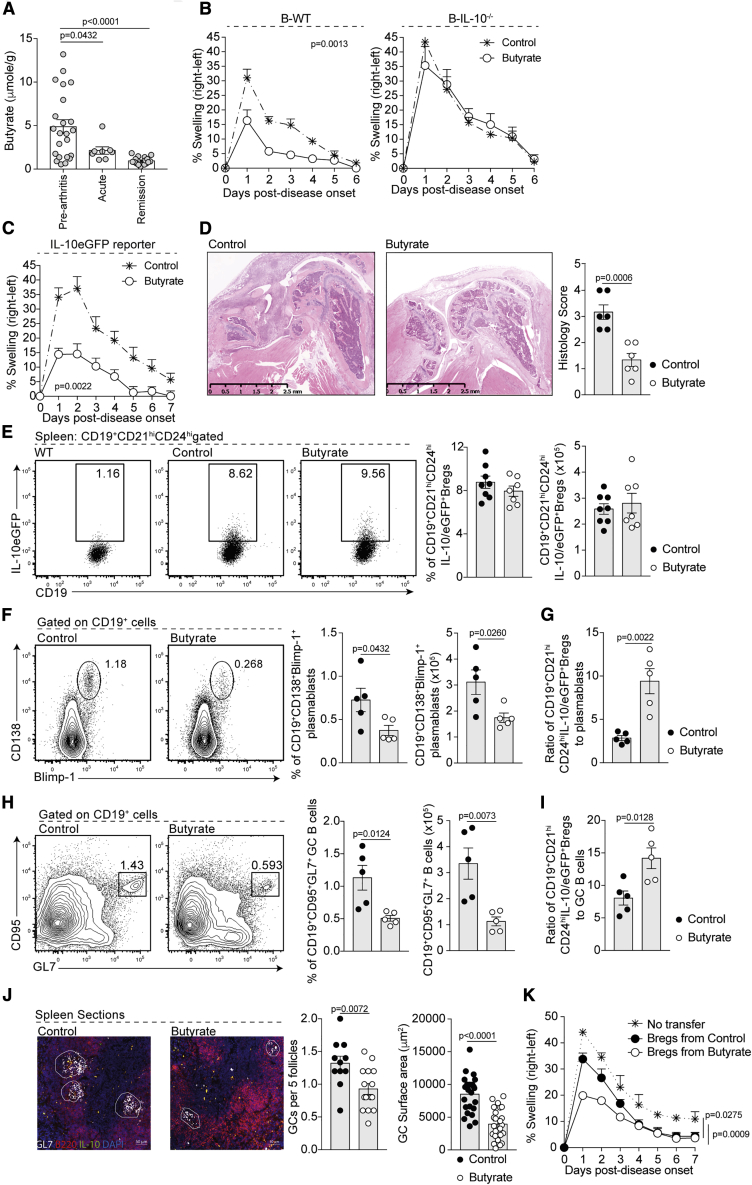
Figure 2.
Butyrate Supplementation Suppresses Arthritis by Skewing the B Cell Compartment in Favor of a Regulatory Phenotype
(A) Stool butyrate levels in WT mice pre-arthritis (n = 23), with acute arthritis (n = 8), and in remission from arthritis (n = 18) as measured by high-performance liquid chromatography (cumulative data are shown).
(B) Mean clinical score of control (cumulative n = 25) and butyrate-supplemented B-WT chimeric mice or B-IL-10−/−chimeric mice (n = 8 per group) (one representative experiment of two experiments is shown); y axis shows percentage swelling in antigen-injected knee compared to control knee.
(C) Mean clinical score of control (cumulative n = 15) and butyrate-supplemented IL-10eGFP reporter mice (cumulative n = 13); y axis shows percentage swelling in antigen-injected knee compared to control knee (one representative experiment of two experiments is shown).
(D) Representative H&E staining of knee joints from control and butyrate-supplemented IL-10eGFP reporter mice (left) and blinded histology scores (right) of joint damage.
(E) Representative flow cytometry plots (left) and bar charts (right) showing CD19+CD21hiCD24hiIL-10eGFP+Breg frequency and number in control (cumulative n = 15) and butyrate-supplemented mice (cumulative n = 13) (one representative experiment of three experiments is shown).
(F) Representative flow cytometry plots (left) and bar charts (right) showing CD19+CD138+Blimp-1+plasmablast frequency and number in control and butyrate-supplemented mice (cumulative n = 11 per group, one representative experiment of two experiments is shown).
(G) Bar charts show ratio of CD19+CD21hiCD24hiIL-10eGFP+Bregs to plasmablast in control and butyrate-supplemented mice (cumulative n = 11 per group, one representative experiment of two experiments is shown).
(H) Representative flow cytometry plots (left) and bar chart (right) shows the percentage and number of CD19+CD95+GL7+ germinal center (GC) B cells in control and butyrate-supplemented mice (cumulative n = 11 per group, one representative experiment of three experiments is shown).
(I) Bar chart shows ratio of CD19+CD21hiCD24hiIL-10eGFP+Bregs to GC B cells in control and butyrate-supplemented mice (cumulative n = 11, one representative experiment of two experiments is shown).
(J) Representative immunofluorescence blinded histological analysis of the number and size of GC control and butyrate-supplemented mice (original magnification 20×, n = 3).
(K) Mean clinical score following transfer of CD19+CD21hiCD24hiIL-10eGFP+Bregs from control (cumulative n = 6) or butyrate-supplemented mice (cumulative n = 6), a control group that did not receive a transfer; y axis shows percentage swelling in antigen-injected knee compared to control knee (cumulative n = 8) (one representative experiment of two experiments is shown).
Cells were isolated at day 7 post-disease onset. Data represent mean ± SE (A, one-way ANOVA; B, C, and K, two-way ANOVA; D–J, Student’s t test). See also Figures S2–S4.