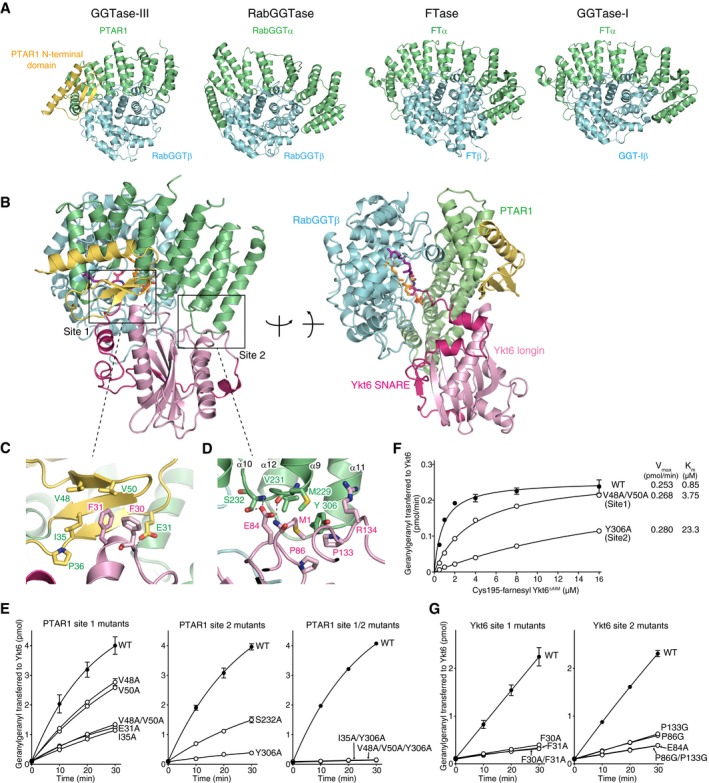
-
A
Structural comparison of GGTase‐III and other prenyltransferases. The α and β subunits of the prenyltransferases are shown in green and cyan, respectively. The unique N‐terminal domain of PTAR1 is shown in yellow.
-
B
Overall structure of GGTase‐III complexed with Cys195‐farnesyl Ykt6ΔAIM and GGPP in two orientations. GGTase‐III is colored as in (A). The longin domain of Ykt6 is in pink, and SNARE domain is in magenta.
-
C, D
Magnified views of site 1 (C) and site 2 (D) depicting the interaction between PTAR1 and Ykt6. Dashed lines indicate hydrogen bonds.
-
E
Geranylgeranylation activity of WT GGTase‐III and the indicated mutants (100 nM each). Cys195‐farnesyl Ykt6ΔAIM (1 μM) and 3H‐GGPP (1 μM) were used as substrates (mean ± SEM, n = 3).
-
F
Kinetic analysis of WT GGTase‐III and the site 1 or site 2 mutant (100 nM each) using increasing concentrations of Cys195‐farnesyl Ykt6ΔAIM (mean ± SEM, n = 3 for WT and Y306A, n = 1 for V48A/V50A).
-
G
Geranylgeranylation of unprenyl WT Ykt6 and the site 1 or site 2 mutants by GGTase‐III. WT and mutant Ykt6 proteins (5 μM each) were incubated with GGTase‐III (100 nM) and 3H‐GGPP (1 μM), and the amount of 3H‐geranylgeranyl transferred to Ykt6 was quantified (mean ± SEM, n = 3).