Figure 7. GGTase‐III‐deficient cells exhibit structural and functional Golgi defects.
-
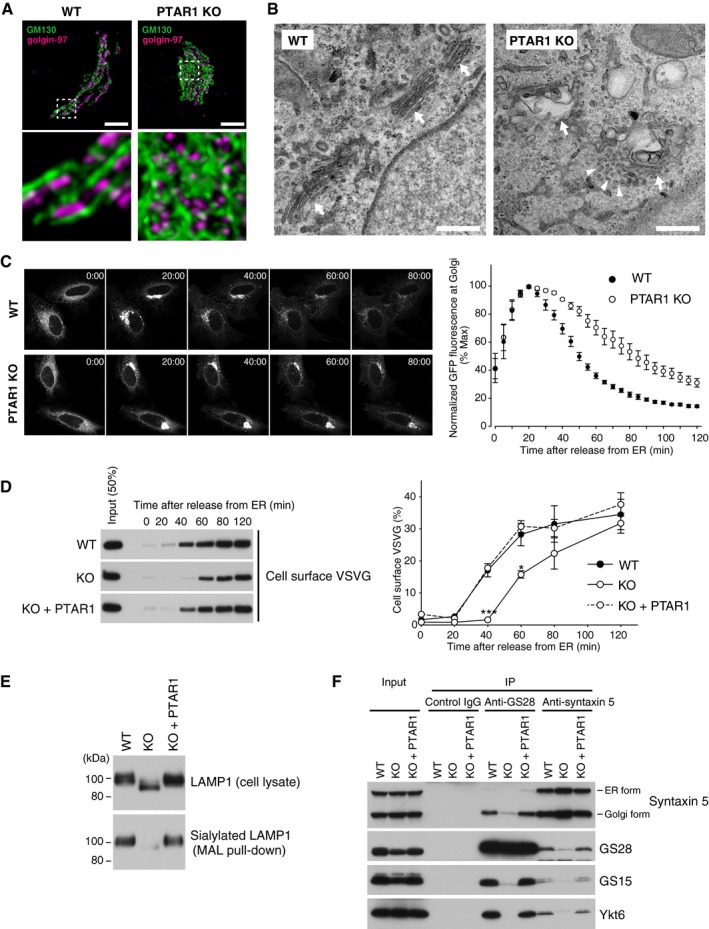
ARepresentative confocal images of the Golgi apparatus in WT or PTAR1 KO HeLa cells. Cells were co‐immunostained for GM130 (a cis‐Golgi marker) and golgin‐97 (a trans‐Golgi marker). Images were deconvoluted using Huygens software. The lower panels show magnified images of the boxed region of the upper panels. Scale bars, 5 μm.
-
BElectron micrographs of the Golgi apparatus in WT or PTAR1 KO HAP1 cells. Arrows indicate Golgi stacks. Arrowheads indicate examples of unfused vesicles accumulated around the swollen Golgi cisternae in PTAR1 KO cells. Scale bars, 500 nm.
-
C, DDefect in intra‐Golgi trafficking in PTAR1 KO cells. (C) VSVG‐GFP expressing WT and PTAR1 KO HeLa cells were cultured at 40°C and then shifted to 32°C. VSVG‐GFP fluorescence images taken at the indicated times after the temperature shift are shown. The right panel shows quantification of VSVG‐GFP fluorescence in the Golgi region after the temperature shift (mean ± SEM, n = 6). (D) VSVG‐GFP expressing WT HeLa cells, PTAR1 KO HeLa cells, and PTAR1 KO HeLa cells stably expressing PTAR1 (KO + PTAR1) were cultured at 40°C and then shifted to 32°C. At the indicated time points, cell surface proteins were biotinylated using sulfo‐NHS‐LC‐biotin. Biotinylated VSVG‐GFP was purified from cell lysates using avidin agarose and analyzed by immunoblotting with anti‐GFP antibody. The right panel shows quantification of the cell surface biotinylated VSVG‐GFP (means ± SEM, n = 3). Data were analyzed by one‐way ANOVA with Dunnett's post‐hoc test. *P < 0.05, ***P < 0.001.
-
EAnalysis of LAMP1 glycosylation. Cell lysates of WT HeLa cells, PTAR1 KO HeLa cells, and PTAR1 KO HeLa cells stably expressing PTAR1 (KO + PTAR1) were analyzed by immunoblotting with anti‐LAMP1 antibody (upper). Sialylated LAMP1 was precipitated from the cell lysates using Maackia amurensis leucoagglutinin (MAL) agarose and analyzed by immunoblotting (lower).
-
FDefect in the Golgi SNARE assembly in PTAR1 KO cells. The Golgi SNARE complex was immunoprecipitated from NEM‐treated WT HAP1 cells, PTAR1 KO HAP1 cells, and PTAR1 KO HAP1 cells stably expressing PTAR1 (KO + PTAR1) using control mouse IgG, anti‐GS28 IgG, or anti‐syntaxin 5 IgG. Immunoprecipitates were analyzed by immunoblotting with antibodies against syntaxin 5, GS28, GS15, and Ykt6. Syntaxin 5 has two isoforms with different translation initiation sites. Inputs were 20% (syntaxin 5, GS28, and GS15) and 2% (Ykt6). The data shown are representative of three independent experiments with similar results.
Source data are available online for this figure.
