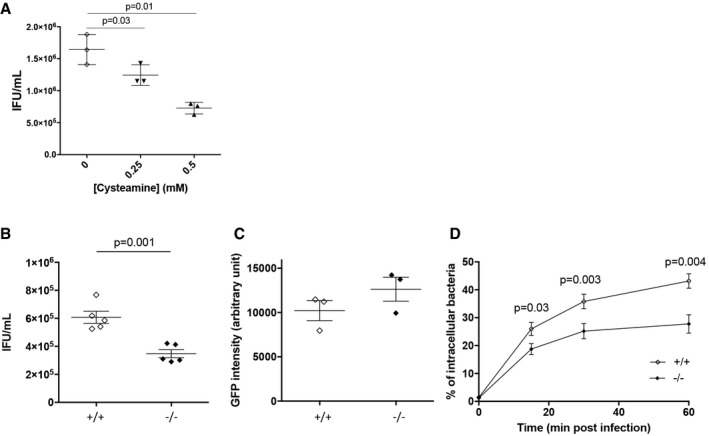
Figure EV1. TG2 is beneficial for bacterial development (related to Fig 2).
-
AHeLa cells were pre‐treated with the indicated concentrations of cysteamine for 2 h before being infected with L2incDGFP at MOI = 0.15. Thirty hours later, the cells were disrupted and bacterial titers (IFU) were determined by re‐infecting fresh HeLa cells as described in the methods. The mean ± SD of three independent experiments is shown. P‐values of Student's paired t‐test are indicated.
-
BTG2+/+ and TG2−/− MEFs were infected with L2incDGFP at MOI = 0.15. Thirty hours later, the cells were disrupted and bacterial titers were determined by re‐infecting fresh TG2+/+ cells as described in the methods. The mean ± SD of five independent experiments and P‐value from Student's paired t‐test are shown.
-
CTo measure bacterial adhesion, TG2+/+ and TG2−/− MEFs were incubated at 4°C for 4 h with L2incDGFP at MOI = 10 before being washed and fixed as described in the methods. The mean ± SD of three independent experiments is shown.
-
DTG2+/+ and TG2−/− MEFs were infected with L2incDGFP at MOI = 10 and fixed at the indicated time. Extracellular bacteria were differentially labeled as described in the methods. The mean ± SD of three independent experiments, and P‐values from Student's paired t‐test, is shown.
