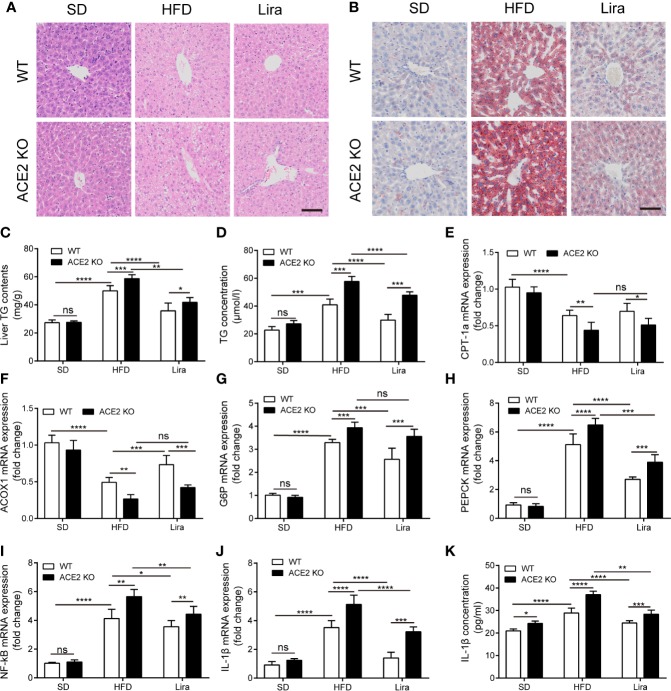
Figure 3.
Liraglutide ameliorates hepatic steatosis with suppressed gluconeogenesis and inflammation in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) wild type (WT) mice. HE staining (A) and Oil red O staining (B) of liver tissues; Scale bars = 50 μm. (C) the statistical charts of TG content in liver tissues; (D) Serum TG concentration. (E, F) Relative mRNA expressions of fatty acid oxidation-related genes ACOX-1 (E) and CPT-1a (F) in livers were measured by quantitative PCR (qPCR). (G–J) Relative mRNA expressions of gluconeogenesis-related genes G6P (G) and PEPCK (H), as well as inflammation-related genes NF-κB (I) and IL-1β (J) in livers. (K) Serum IL-1β concentration. n=7. Data are expressed as the mean ± SD. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, and ****P < 0.0001. Ns, no statistical difference.