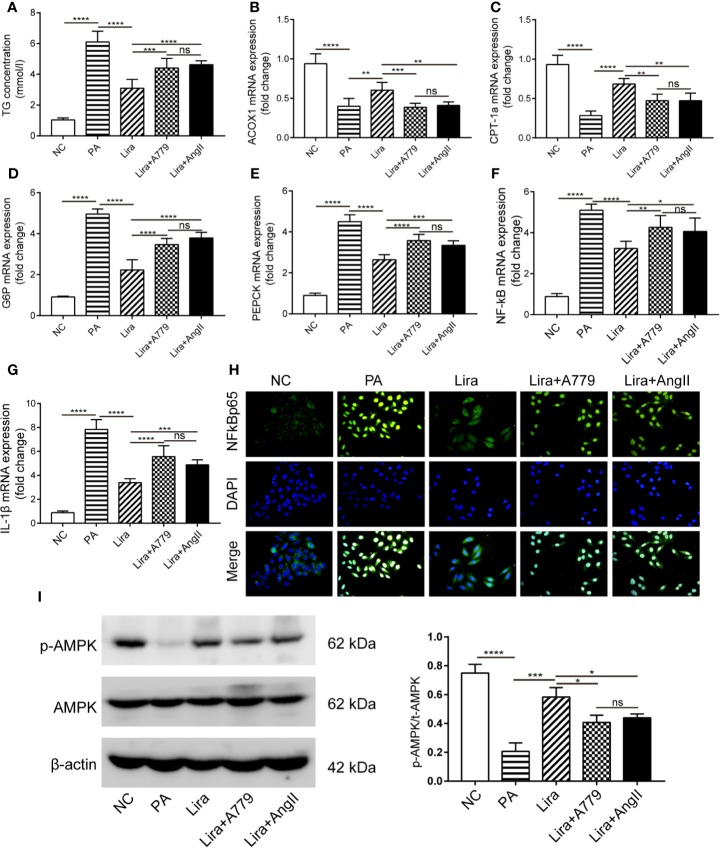
Figure 5.
A blockage of the ACE2/Ang1-7/Mas axis attenuates liraglutide-mediated benefits on hepatocellular steatosis and gluconeogenesis, as well as inflammation and related AMPK signaling pathways in HepG2 cells. HepG2 cells were treated with or without PA (0.25 mmol/L) in the presence or absence of liraglutide (100 nmol/L) or liraglutide (100 nmol/L) + A779 (10-7 mol/L) combination or liraglutide (100 nmol/L) + AngII (100 nmol/L) for 24 h. (A) The statistical charts of TG content in HepG2 cells. (B–G) Relative mRNA expression of ACOX-1 (B), CPT-1a (C) and G6P (D), PEPCK (E) as well as NF-κB (F), IL-1β (G) in HepG2 cells was measured by qPCR; (H) Nuclear translocation of NF-κB p65 in HepG2 cells was measured by immunofluorescence staining; magnification, 400. (I) Western blotting of AMPK phosphorylation in HepG2 cells. n=3. Data are expressed as the mean ± SD. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, and ****P < 0.0001. Ns, no statistical difference.