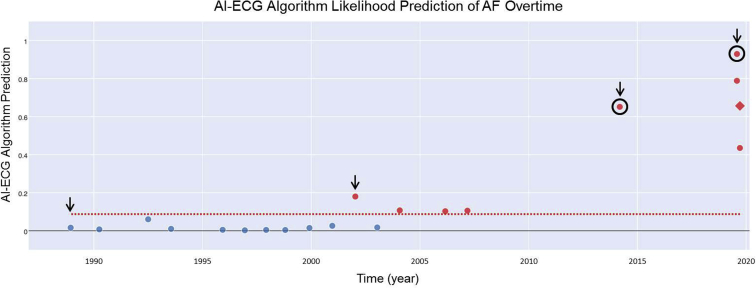
Figure 2.
Retrospective artificial intelligence–enabled electrocardiogram (AI-ECG) analysis of the patient’s available ECGs in our electronic medical record over a 24-year period. Our current algorithm5 provides an alert to the provider for an abnormal ECG when a likelihood prediction value of greater than 8.70% (dotted red line) is projected. All abnormal ECGs are designated by a red marker in the figure. In this case, the first abnormal ECG would have been reported over 12 years prior to the patient’s first thromboembolic event. The first and second thromboembolic events are circled in black. The black arrows correspond to the ECGs depicted in Figure 1. The red diamond-shaped marker indicates when atrial flutter was recorded (Figure 3). AF = atrial fibrillation.