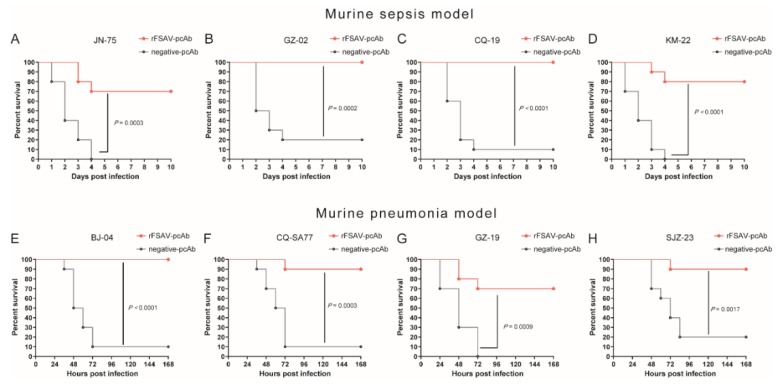
Figure 6.
rFSAV-pcAb broadly protected mice from different clinical S. aureus strains challenge in murine sepsis and pneumonia models. (A–D) Protection of passive immunization with rFSAV-pcAbs in the mouse sepsis model. BALB/c mice (n = 10) were injected intravenously with 100 μL of rFSAV-pcAbs or negative-pcAbs (20 mg/mL). Two hours later, the mice were challenged with JN-75, CQ-19, GZ-02 or KM-22 (3.0 × 108, 5.0 × 108, 7.0 × 108 or 2.0 × 108 CFUs/mouse, respectively) by tail intravenous injection. The survival rate was monitored for 10 days. (E–H) Protection of passive immunization with rFSAV-pcAbs in the mouse pneumonia model. C57BL/6 mice (n = 10) were injected intravenously with 100 μL of rFSAV-pcAbs or negative-pcAbs (20 mg/mL). Two hours later, the mice were challenged with BJ-04, CQ-SA77, GZ-19 or SJZ-23 (9.0 × 108, 4.0 × 108, 3.0 × 108 or 4.0 × 108 CFUs/mouse, respectively) by intratracheal injection. The survival rates were recorded every 12 h over a 7-day observation period post challenge. (A–H) The Mantel-Cox log-rank test was used to compare differences between passive immunization and control groups.