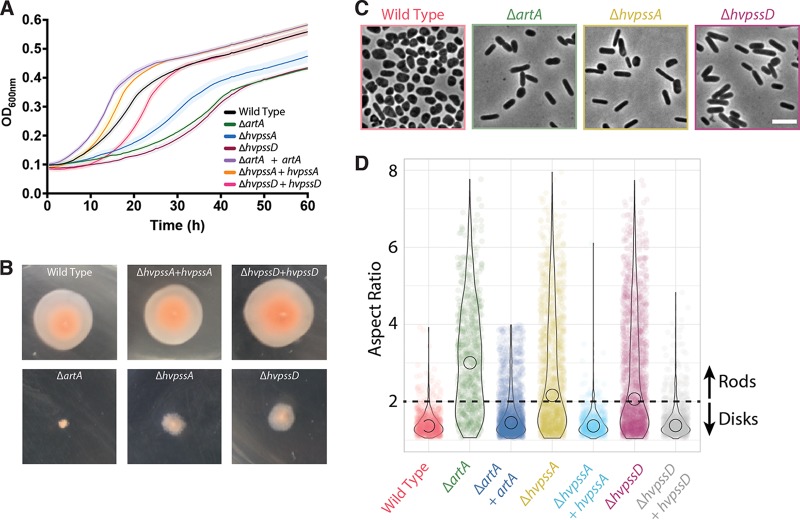
FIG 2.
Absence of HvPssA or HvPssD leads to defects in growth, cell morphology, and motility. (A) Wild-type (strain H53) and ΔartA, ΔhvpssA, and ΔhvpssD mutant cells were grown with shaking in 96-well plates with a total volume of 200 μl of liquid semidefined CA medium, and the growth of six biological replicates was monitored at the OD600, with recordings taken every 30 min. For complementation analysis, artA, hvpssA, or hvpssD was expressed from pTA963 under the tryptophan-inducible p.tna promoter. The wild-type and deletion strains were transformed with an empty pTA963 plasmid as a control. (B) The wild-type (strain H53) and artA, hvpssA, or hvpssD deletion and complementation strains from individual colony on solid agar plates were individually stab inoculated with a toothpick into semisolid 0.35% agar in CA medium supplemented with tryptophan, followed by incubation at 45°C. (C) Phase-contrast images were taken from wild-type and mutant cells during mid-exponential-growth phase (OD600, 0.3) and immobilized under 0.5% agarose pads. (D) Violin distributions of aspect ratio measurements from single cells. Rodlike (aspect ratio, >2) cells were prevalent to disklike (aspect ratio, <2) cells in the mutant strains compared to the wild type. Biological replicates were collected on three different days, and data were analyzed from >1,000 cells under each condition by automated image segmentation. Scale bars = 5 μm.