FIG 3.
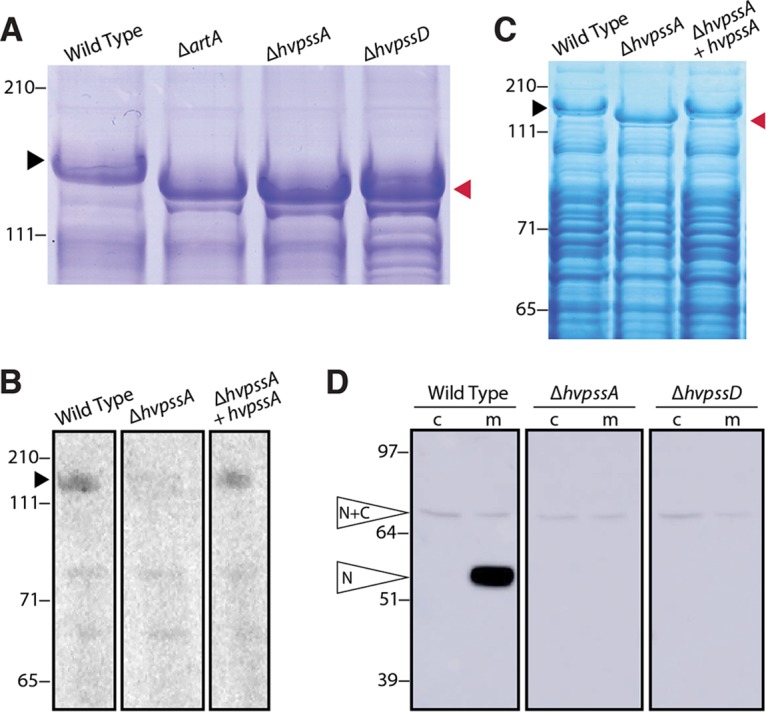
HvPssA and HvPssD are critical for HVO_0405 C-terminal processing and SLG lipidation. (A) Coomassie-stained LDS-PAGE gel of cell extracts from H. volcanii H53 (wild-type [WT]) and ΔartA, ΔhvpssA, and ΔhvpssD mutant strains. The ΔartA, ΔhvpssA, and ΔhvpssD mutant SLG (red arrowhead) exhibited a mobility shift compared to the WT SLG (black arrowhead). (B) Fluorography of protein extracts isolated from H53 (WT), ΔhvpssA mutant, and hvpssA complementation (ΔhvpssA + hvpssA) cells grown in the presence of 1 μCi/ml [14C]mevalonic acid. Significant labeling of SLG (black arrowhead) is only detected in the WT and hvpssA complementation (ΔhvpssA + hvpssA) extracts. (C) Coomassie staining of the gel used for fluorography. The SLG mobility shift in the ΔhvpssA mutant (red arrowhead) is reverted upon hvpssA expression in trans. (D) Western blot analysis of cytoplasmic (c) and membrane (m) fractions of H53 (WT), ΔhvpssA mutant, and ΔhvpssD mutant strains expressing, in trans, HVO_0405-6×His. The N-terminal domain of HVO_0405 was detected using anti-HVO_0405-N-term antibodies. Hvo_0405 not processed by ArtA and the N-terminal HVO_0405 processed by ArtA are labeled “N+C” and “N,” respectively. The C-terminal domain, which carries a His tag, has not been analyzed in this experiment. Numbers indicate molecular mass in kilodaltons.
