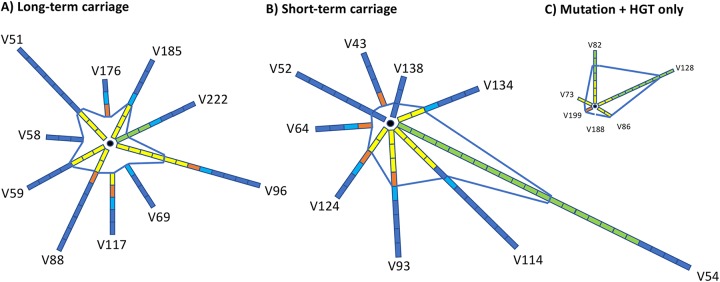
FIG 7.
Relative contributions of LH, mutation, and horizontal gene transfer to functional variation during persistent meningococcal carriage. These diagrams depict the relative amounts of different types of genetic variation occurring during natural asymptomatic carriage of meningococci in 23 university students. Each spoke represents the proportion and type of variation relative to a different but homogeneous starting population, indicated by the black circle. We show only genetic variation that alters the amino acid sequence or expression state of genes and has been putatively or probably fixed in the population (note that fixation was determined by comparison of multiple colonies and time points for all PV and the majority of mutation and HGT events). Each rectangle represents either a single gene or a recombination fragment containing one or more variable genes. The rectangles are colored coded to represent different types of recombination events: dark blue, PV; light blue, antigenic variation of the PilE protein; orange, indel; yellow, mutation; green, recombination due to horizontal gene transfer. The blue lines separate events affecting outer membrane proteins or structures on the outside from other functional groups on the inside. (A) Long-term carriage of 5 to 6 months; (B) short-term carriage of 1 to 3 months; (C) carriers where only mutation and HGT has been assessed.