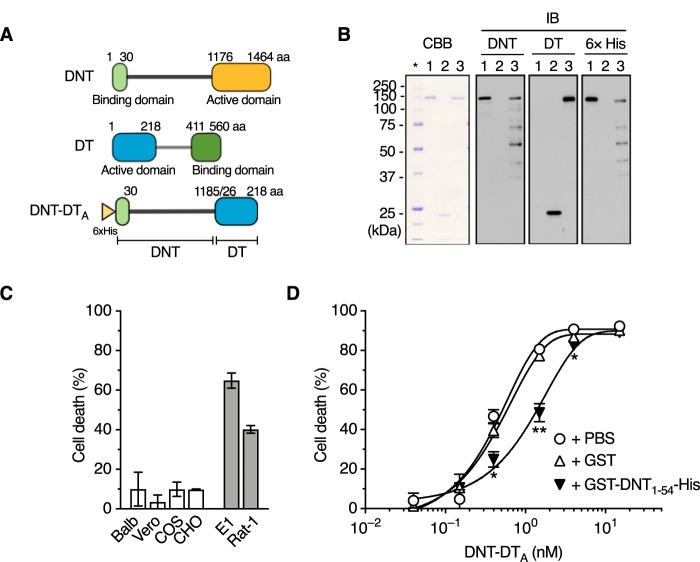
FIG 1.
Construction of DNT-DTA. (A) Schematic representation of DNT-DTA. aa, amino acids. (B) SDS-PAGE and immunoblotting of the purified preparations of DNT, DTA, and DNT-DTA. DNT (lane 1), DTA (lane 2), and DNT-DTA (lane 3) were applied at 0.5 μg/lane for Coomassie brilliant blue R250 (CBB) staining and at 0.1 μg/lane, 0.2 μg/lane, and 0.2 μg/lane, respectively, for immunoblotting (IB). The samples were probed with an anti-DNT polyclonal antibody, an anti-DT polyclonal antibody, and an anti-His tag antibody. The asterisk indicates the lane for marker proteins. Note that DNT-DTA was recognized by anti-DNT and anti-DT antibodies. (C) Sensitivity of cultured cells to DNT-DTA. DNT-resistant (white bars, Balb3T3, Vero, COS7, and CHO-K1) and -sensitive (gray bars, MC3T3-E1 and Rat-1) cells were incubated with DNT-DTA for 16 h, and the rate of cell death was measured. (D) Competitive inhibition of cytotoxicity of DNT-DTA with GST (glutathione S-transferase)-DNT1–54-His. MC3T3-E1 cells were treated with DNT-DTA in the presence of 400 nM GST or GST-DNT1–54-His, and the rate of cell death was measured. *, P < 0.01; **, P < 0.001 (compared to PBS). Plotted data represent means ± standard errors of the means (SEM) (n = 3) (C and D).