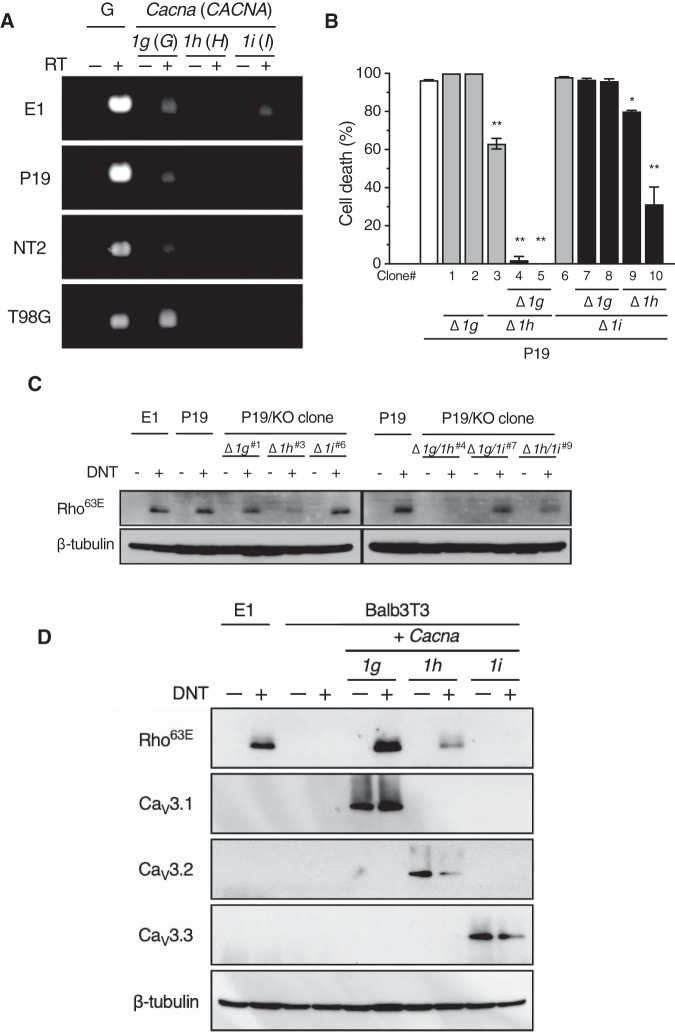
FIG 5.
Sensitivity of isotypes of the calcium ion channels to DNT. (A) RT-PCR analyses of T-type Ca2+ channel transcripts (Cacna1g, Cacna1h, and Cacna1i for MC3T3-E1 and P19 cells of mouse origin and CACNA1G, CACNA1H, and CACNA1I for NT2 and T98G cells of human origin). RT, reverse transcription reaction; G, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (Gapdh or GAPDH) (positive control). (B and C) Sensitivity of P19 cells deficient in Cacna1g (Δ1g), Cacna1h (Δ1h), and/or Cacna1i (Δ1i) to DNT-DTA (B) and DNT (C). The cells were treated with DNT-DTA or DNT and subjected to a cytotoxicity assay (B) or immunoblotting for deamidated Rho (C), respectively. Each bar represents the mean ± SEM (n = 3). *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.0001 (versus parental P19 cells [B]). The numbers of selected clones in panel C correspond to those shown in panel B. KO, knockout. (D) DNT sensitivity of Balb3T3 cells expressing the isotypes of the T-type voltage-gated Ca2+ channels. The cells were treated with DNT and subjected to SDS-PAGE followed by immunoblotting for deamidated Rho (Rho63E), CaV3.1, CaV3.2, CaV3.3, and β-tubulin.