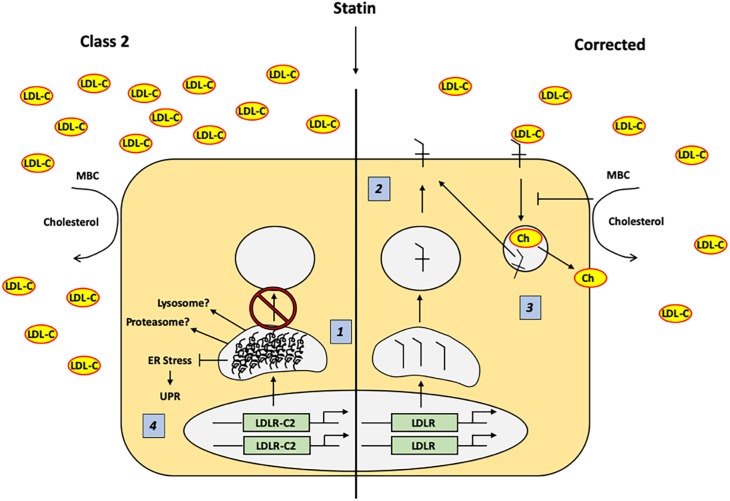
Fig. 5.
Response to statin treatment in class II LDLR and corrected iPSC and HLC. (1) Treatment with 5 μM RS causes uniform upregulation of class II and corrected LDLR gene transcription, but results in an accumulation of misfolded immature (120 kDa) LDLR protein as well as greater total LDLR (120 kDa+160 kDa) in class II compared to corrected cells. (2) Corrected LDLR is transported from the ER to the Golgi and on to the plasma membrane, where it participates in receptor-medicated LDL-C internalization. (3) When cellular cholesterol is removed by MBC treatment, LDLR-mediated endocytosis and recycling is inhibited, delaying LDL-C internalization kinetics. (4) Class II LDLR mutations accumulate as misfolded protein in the ER when treated with 5 μM rosuvastatin, but this accumulation does not appear to cause ER stress and induction of the UPR. Ch, cholesterol; ER, endoplasmic reticulum; LDL-C, low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol; LDLR, LDL receptor; LDLR-CII, class II LDL receptor; MBC, methyl-β-cyclodextrin; UPR, unfolded protein response.