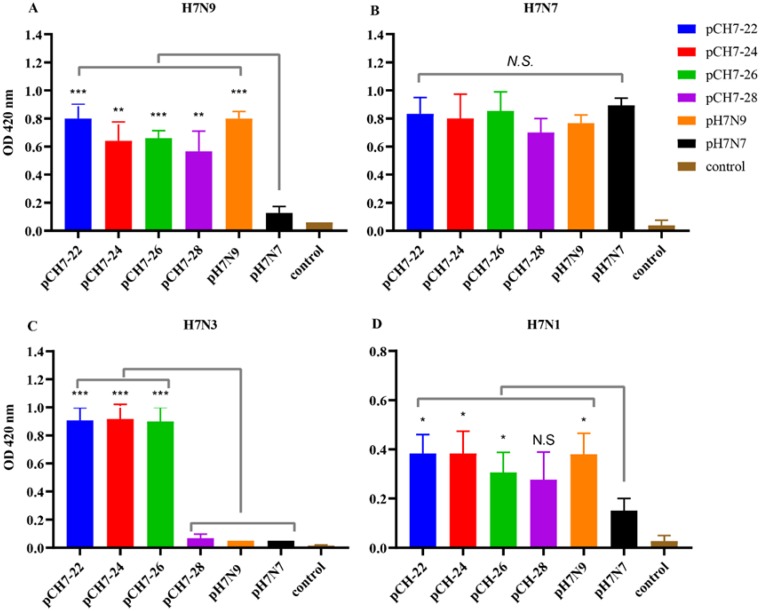
Figure 4.
DNA vaccines encoding consensus H7 proteins elicit broadly reactive antibody responses in mice. Six to 8-week-old female BALB/c mice (10 mice per group) were immunized twice with a 3-week interval. Each vaccination consisted of 30 μg pCH7-22, pCH7-24, pCH7-26, pCH7-28, pH7N9, and pH7N7 dissolved in 30 μL Tris-EDTA buffer. Two weeks after the second immunization, sera were collected from four to five mice per group and treated with an RDE. The treated serum was tested for the titer of total IgG antibodies. An ELISA was performed using a 96-well plate coated with H7N9 (A), H7N7 (B), H7N3 (C), and H7N1 (D) (4 HAU/well), followed by incubation with serial dilutions of RDE-treated serum and then goat anti-mouse IgG (γ-chain specific) conjugated with HRP. The amount of chromogen produced was measured at 1: 100 serum dilution based on the absorbance at 420 nm using an ELISA reader (Synergy H1, Biotek). The data are shown as the mean antibody titers of four mice in each group with standard errors (error bars). Statistical significance was analyzed by t test. p values shown in bar charts and N.S. indicates no significance between two compared groups. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01 and *** p < 0.001 between indicated groups.