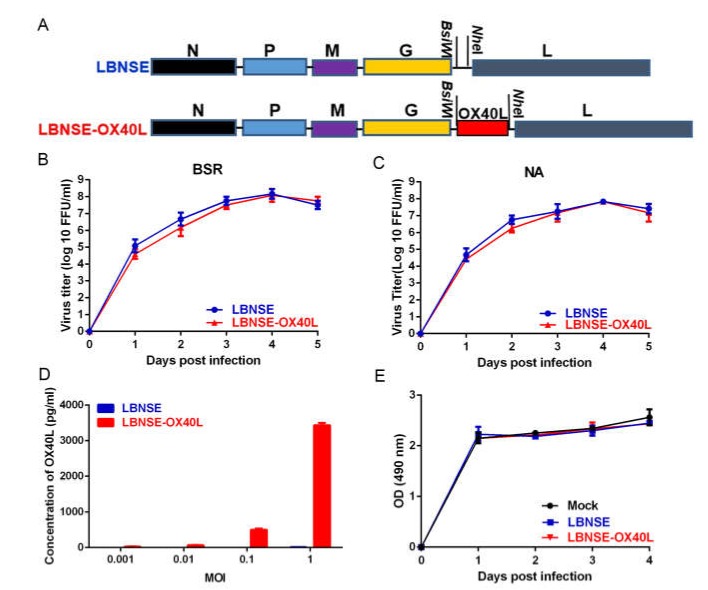
Figure 1.
Characterization of recombinant rabies viruses (rRABV) expressing OX40-ligand (OX40L) in vitro. (A) Construction diagram of LBNSE and LBNSE-OX40L. The vector pLBNSE was derived from the pseudogene-deleted SAD-B19 strain. The BsiWI and NheI sites were introduced between G and L genes. N, P, M, G, and L represented RABV nucleoprotein, phosphoprotein, matrix, glycoprotein, and polymerase genes, respectively. Murine OX40L was inserted into this LBNSE genome in place of the deleted pseudogene. Supernatants of the cells infected with different rRABVs at a MOI = 0.01 were collected at 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5 dpi to determine the titers of LBNSE and LBNSE-OX40L. Based on it, multiple-step growth curves of LBNSE and LBNSE-OX40L, respectively, infecting BSR cells (B) and NA cells (C) were developed. (D) The expression level of mouse OX40L in the infected cell supernatants was detected by ELISA kits. (E) Detection of cell viability of rRABV-infected BSR cells. Error bars represented the standard deviation (SD, n = 3).