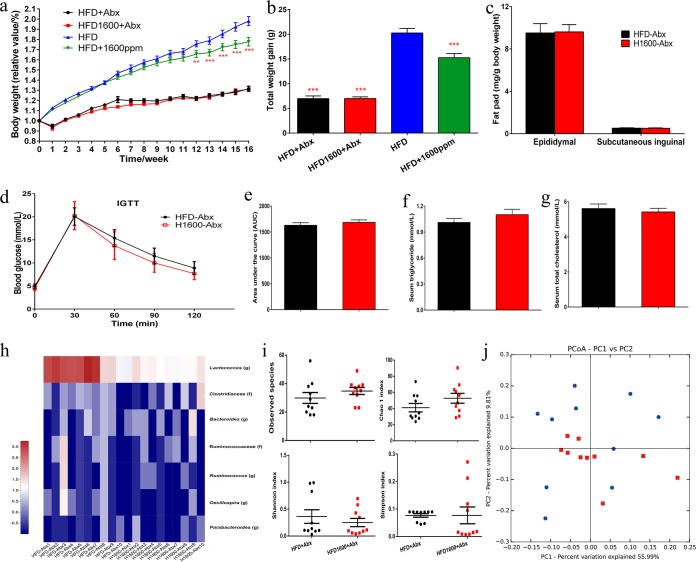
FIG 6.
Continuous antibiotic treatment abrogated the metabolic improvement induced by GML supplementation in HFD-fed mice. Mice were fed an HFD supplemented with antibiotic treatment and given (H1600-Abx) or not given (HFD-Abx) 1,600 mg/kg GML for 16 weeks. The GML-treated group exhibited no significant difference in body weight curves (a), total weight gain (b), or fat pad weight (c) from those of HFD controls under antibiotic treatment. Insulin sensitivity also demonstrated no significant change between these two groups. (d) Mice were fasted overnight (12 h) for an IGTT (2 g/kg body weight). (e) The AUCs of the IGTTs were evaluated. Serum hyperlipidemia, including the levels of serum triglyceride (f) and serum total cholesterol (g), was not significantly altered. Additionally, continuous antibiotic treatment also abolished the gut microbiota alterations induced by GML supplementation. (h) Heatmap demonstrating the abundances of detected bacterial taxa which were significantly changed by GML treatment in HFD-fed mice after antibiotic treatment. (i) α-Diversities for observed species, Chao 1 indexes, Shannon indexes, and Simpson indexes. (j) Unweighted UniFrac PCoA plot based on OTU abundance. Fourteen to 15 mice (a to g) and 10 mice (h to j) were tested. Data are expressed as means ± SEM. Values with asterisks are significantly different based on a one-way analysis of variance with Tukey’s post hoc test (*, P < 0.05 versus HFD controls; **, P < 0.01 versus HFD controls; ***, P < 0.001 versus HFD controls).